Burying Hatchets into Endemic Diagnoses: Disseminated Blastomycosis from a Potentially Novel Occupational Exposure
- PMID: 37505667
- PMCID: PMC10385565
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed8070371
Burying Hatchets into Endemic Diagnoses: Disseminated Blastomycosis from a Potentially Novel Occupational Exposure
Abstract
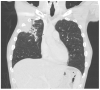
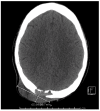
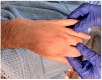
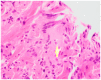
Background: Blastomycosis is an endemic fungal disease predominantly observed in the northern regions of North America. It manifests primarily as pulmonary disease but can also involve dissemination to the skin, bones, and genitourinary tract. Detailed Case Description: We describe a case of a patient in Southern California with disseminated blastomycosis following his occupational exposure to decaying wood. The patient was treated with intravenous amphotericin therapy followed by oral itraconazole therapy with full resolution of his symptoms.
Conclusions: The patient's case presentation serves as a reminder regarding Blastomyces infections diagnosed outside of endemic regions and suggests a potential link between blastomycosis and a novel occupational exposure surrounding axe throwing.
Keywords: Blastomyces dermatitidis; axe throwing; blastomycosis; endemic fungi; occupational exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wheat J., Wheat H., Connolly P., Kleiman M., Supparatpinyo K., Nelson K., Bradsher R., Restrepo A. Cross-reactivity in Histoplasma capsulatum variety capsulatum antigen assays of urine samples from patients with endemic mycoses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997;24:1169–1171. doi: 10.1086/513647. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention Sources of Histoplasmosis. National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases, Centers of Diseases Control and Prevention. [(accessed on 26 May 2023)];2023 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/histoplasmosis/causes.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

