Effect of Classical Music on Depth of Sedation and Induction Propofol Requirements in Dogs
- PMID: 37505838
- PMCID: PMC10383266
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci10070433
Effect of Classical Music on Depth of Sedation and Induction Propofol Requirements in Dogs
Abstract
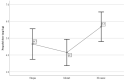
The main objective of this prospective, randomized, blind, cross-over experimental study was to evaluate the effect of classical music on the depth of sedation and propofol requirements for the induction of anaesthesia in dogs. Twenty dogs were involved, and each was subjected to three different treatments with a 3-month gap: Chopin music, Mozart music, and no music, via loudspeakers. The dogs were premedicated with acepromazine and butorphanol by intramuscular injection, and anaesthesia was induced using propofol intravenously. To compare the depth of sedation and propofol requirements for the induction of anaesthesia among the different treatments, we utilized non-parametric tests (Kruskal-Wallis test) for the depth of sedation due to a slight deviation from the normal distribution and parametric (ANOVA) for propofol requirements. When exposed to music (Chopin or Mozart), dogs exhibited deeper sedation and required less propofol for their intubation compared to the no-music treatment (p < 0.05). Exposure to classical music had a positive impact on the level of sedation, and more profound central nervous system depression seemed to contribute to approximately 20% lower propofol dose requirements for tracheal intubation. Therefore, classical music during the preoperative period appeared to exert a beneficial effect, at least when applying the specific pre-anaesthetic medications used in the present study.
Keywords: acepromazine; butorphanol; dog; music; propofol; sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of classical music on light-plane anaesthesia and analgesia in dogs subjected to surgical nociceptive stimuli.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 22;14(1):19511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70343-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39174615 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of sedation scores and propofol induction doses in dogs after intramuscular premedication with butorphanol and either dexmedetomidine or medetomidine.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013 Nov;40(6):584-9. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12072. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23889781 Clinical Trial.
-
The use of propofol for induction of anaesthesia in dogs premedicated with acepromazine, butorphanol and acepromazine-butorphanol.N Z Vet J. 1997 Aug;45(4):129-34. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1997.36012. N Z Vet J. 1997. PMID: 16031972
-
Effects of intravenous acepromazine and butorphanol on propofol dosage for induction of anesthesia in healthy Beagle dogs.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2022 Jul;49(4):354-363. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2022.03.002. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2022. PMID: 35606286
-
Propofol anesthesia.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1999 May;29(3):747-78. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(99)50059-4. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1999. PMID: 10332821 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of classical music on light-plane anaesthesia and analgesia in dogs subjected to surgical nociceptive stimuli.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 22;14(1):19511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70343-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39174615 Free PMC article.
-
Proposed Physiological and Neurobiological Mechanisms of Music's Effect, with a Focus on the Perioperative Period: Literature Evidence from Human, Canine and Feline Medicine.Vet Sci. 2025 Aug 17;12(8):770. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12080770. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40872720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

