The transport of mannitol in Sinorhizobium meliloti is carried out by a broad-substrate polyol transporter SmoEFGK and is affected by the ability to transport and metabolize fructose
- PMID: 37505890
- PMCID: PMC10433430
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001371
The transport of mannitol in Sinorhizobium meliloti is carried out by a broad-substrate polyol transporter SmoEFGK and is affected by the ability to transport and metabolize fructose
Abstract
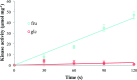
The smo locus (sorbitol mannitol oxidation) is found on the chromosome of S. meliloti's tripartite genome. Mutations at the smo locus reduce or abolish the ability of the bacterium to grow on several carbon sources, including sorbitol, mannitol, galactitol, d-arabitol and maltitol. The contribution of the smo locus to the metabolism of these compounds has not been previously investigated. Genetic complementation of mutant strains revealed that smoS is responsible for growth on sorbitol and galactitol, while mtlK restores growth on mannitol and d-arabitol. Dehydrogenase assays demonstrate that SmoS and MtlK are NAD+-dependent dehydrogenases catalysing the oxidation of their specific substrates. Transport experiments using a radiolabeled substrate indicate that sorbitol, mannitol and d-arabitol are primarily transported into the cell by the ABC transporter encoded by smoEFGK. Additionally, it was found that a mutation in either frcK, which is found in an operon that encodes the fructose ABC transporter, or a mutation in frk, which encodes fructose kinase, leads to the induction of mannitol transport.
Keywords: ABC transporter; Rhizobium; metabolism; polyol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Geddes BA, Oresnik IJ. In: The Mechanistic Benefits of Microbial Symbionts (Advances in Environmental Microbiology Series. Hurst CJ, editor. Vol. 2. Springer International Publishing; 2016. The mechanism of symbiotic nitrogen fixation; pp. 69–97. vol.
-
- Finan TM, Mcwhinnie E, Driscoll B, Watson RJ. Complex symbiotic phenotypes result from gluconeogenic mutations in Rhizobium meliloti . MPMI. 1991;4:386. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-4-386. - DOI
-
- Oresnik IJ, Pacarynuk LA, O’Brien SAP, Yost CK, Hynes MF. Plasmid-encoded catabolic genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii: evidence for a plant-inducible rhamnose locus involved in competition for nodulation. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998;11:1175–1185. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1998.11.12.1175. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

