A comparative study to optimize experimental conditions of pentylenetetrazol and pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in zebrafish larvae
- PMID: 37506089
- PMCID: PMC10381053
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288904
A comparative study to optimize experimental conditions of pentylenetetrazol and pilocarpine-induced epilepsy in zebrafish larvae
Abstract
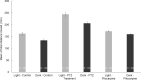
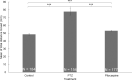
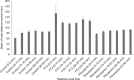
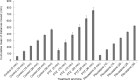
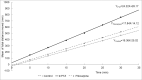
A common way to investigate epilepsy and the effect of antiepileptic pharmaceuticals is to analyze the movement patterns of zebrafish larvae treated with different convulsants like pentylenetetrazol (PTZ), pilocarpine, etc. Many articles have been written on this topic, but the research methods and exact settings are not sufficiently defined in most. Here we designed and executed a series of experiments to optimize and standardize the zebrafish epilepsy model. We found that during the light and the dark trials, the zebrafish larvae moved significantly more in the light, independent of the treatment, both in PTZ and pilocarpine-treated and the control groups. As expected, zebrafish larvae treated with convulsants moved significantly more than the ones in the control group, although this difference was higher between the individuals treated with PTZ than pilocarpine. When examining the optimal observation time, we divided the half-hour period into 5-minute time intervals, and between these, the first 5 minutes were found to be the most different from the others. There were fewer significant differences in the total movement of larvae between the other time intervals. We also performed a linear regression analysis with the cumulative values of the distance moved during the time intervals that fit the straight line. In conclusion, we recommend 30 minutes of drug pretreatment followed by a 10-minute test in light conditions with a 5-minute accommodation time. Our result paves the way toward improved experimental designs using zebrafish to develop novel pharmaceutical approaches to treat epilepsy.
Copyright: © 2023 Szep et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


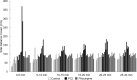
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

