Effects of Early Clozapine Treatment on Remission Rates in Acute Schizophrenia (The EARLY Trial): Protocol of a Randomized-Controlled Multicentric Trial
- PMID: 37506738
- PMCID: PMC10484642
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2110-4259
Effects of Early Clozapine Treatment on Remission Rates in Acute Schizophrenia (The EARLY Trial): Protocol of a Randomized-Controlled Multicentric Trial
Abstract
Background: Quick symptomatic remission after the onset of psychotic symptoms is critical in schizophrenia treatment, determining the subsequent disease course and recovery. In this context, only every second patient with acute schizophrenia achieves symptomatic remission within three months of initiating antipsychotic treatment. The potential indication extension of clozapine-the most effective antipsychotic-to be introduced at an earlier stage (before treatment-resistance) is supported by several lines of evidence, but respective clinical trials are lacking.
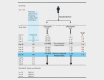
Methods: Two hundred-twenty patients with acute non-treatment-resistant schizophrenia will be randomized in this double-blind, 8-week parallel-group multicentric trial to either clozapine or olanzapine. The primary endpoint is the number of patients in symptomatic remission at the end of week 8 according to international consensus criteria ('Andreasen criteria'). Secondary endpoints and other assessments comprise a comprehensive safety assessment (i. e., myocarditis screening), changes in psychopathology, global functioning, cognition, affective symptoms and quality of life, and patients' and relatives' views on treatment.
Discussion: This multicentre trial aims to examine whether clozapine is more effective than a highly effective second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs), olanzapine, in acute schizophrenia patients who do not meet the criteria for treatment-naïve or treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Increasing the likelihood to achieve symptomatic remission in acute schizophrenia can improve the overall outcome, reduce disease-associated burden and potentially prevent mid- and long-term disease chronicity.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
E. Wagner has been invited to advisory boards from Recordati. W. Strube has received a speaker’s honorarium from Mag&More GmbH and neurocare and was a member of the advisory board of Recordati. A. Hasan has received speakership fees from Lundbeck, Otsuka, Janssen, Rovi, AbbVie and Recordati. He was member of advisory boards of Boehringer Ingelheim, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Janssen, Rovi, and Recordati. M. Lambert has received honoraria for consultancy and speakers’ fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly Deutschland GmbH, Janssen Cilag GmbH, Lundbeck GmbH, Otsuka Pharma GmbH, Roche Deutschland Holding GmbH, Sanovi Aventis, Trommsdorff GmbH & Co. KG, Takeda Pharma Vertrieb GmbH, and is founder of MiNDNET e-Health-Solutions GmbH. P. Falkai is on the advisory boards and receives speaker fees from Janssen, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Servier and Richter B. Langguth has received honoraria for consultancy and speakers’ fees from ANM, AstraZeneca, Autifony Therapeutics, Decibel Therapeutics, Desyncra, Gerson Lehmanns Group, Lundbeck, Merz, MagVenture, Medical Tribune, Neurolite, Neuromod, Novartis, Pfizer, Rovi, Schwabe, Sea Pharma, Servier, Sonova and Sound Therapeutics; All other co-authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn R S, Winter van Rossum I, Leucht S et al. Amisulpride and olanzapine followed by open-label treatment with clozapine in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder (OPTiMiSE): A three-phase switching study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018;5:797–807. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30252-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical