Liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry of anatoxins, including new conjugates and reduction products
- PMID: 37507466
- PMCID: PMC10444699
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-023-04836-y
Liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry of anatoxins, including new conjugates and reduction products
Abstract
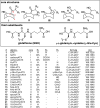
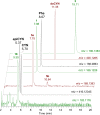
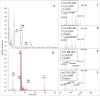
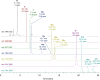
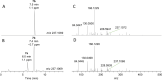
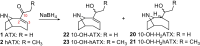
Anatoxins (ATXs) are a potent class of cyanobacterial neurotoxins for which only a handful of structural analogues have been well characterized. Here, we report the development of an LC-HRMS/MS method for the comprehensive detection of ATXs. Application of this method to samples of benthic cyanobacterial mats and laboratory cultures showed detection of several new ATXs. Many of these result from nucleophilic addition to the olefinic bond of the α,β-unsaturated ketone functional group of anatoxin-a (ATX) and homoanatoxin-a (hATX), analogous to the conjugation chemistry of microcystins, which contain similar α,β-unsaturated amide functionality. Conjugates with glutathione, γ-glutamylcysteine, methanethiol, ammonia, methanol and water were detected, as well as putative C-10 alcohol derivatives. Structural confirmation was obtained by simple and selective analytical-scale semisynthetic reactions starting from available ATX standards. Methanol, water and ammonia conjugates were found to result primarily from sample preparation. Reduction products were found to result from enzymatic reactions occurring primarily after cell lysis in laboratory cultures of Kamptonema formosum and Cuspidothrix issatschenkoi. The relative contributions of the identified analogues to the anatoxin profiles in a set of 22 benthic-cyanobacterial-mat field samples were estimated, showing conjugates to account for up to 15% of total ATX peak area and 10-hydroxyanatoxins up to 38%. The developed methodology, new analogues and insight into the chemical and enzymatic reactivity of ATXs will enable a more comprehensive study of the class than possible previously.
Keywords: Anatoxin-a; Cyanobacteria; Cyanotoxin; High-resolution mass spectrometry; LC–HRMS; Non-target analysis.
© 2023. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
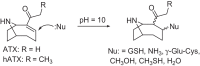
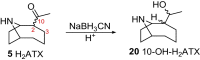


Similar articles
-
Analytical Methods for Anatoxin-a Determination: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;16(4):198. doi: 10.3390/toxins16040198. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid quantitative screening of cyanobacteria for production of anatoxins using direct analysis in real time high-resolution mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan 15;35(1):e8940. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8940. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 32881159
-
Rapid Quantitation of Anatoxins in Benthic Cyanobacterial Mats Using Direct Analysis in Real-Time-High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Oct 4;56(19):13837-13844. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c05426. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36125920 Free PMC article.
-
Production of anatoxin-a and a novel biosynthetic precursor by the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon issatschenkoi.Environ Sci Technol. 2007 Jan 15;41(2):506-10. doi: 10.1021/es061983o. Environ Sci Technol. 2007. PMID: 17310714
-
Ligand-binding assays for cyanobacterial neurotoxins targeting cholinergic receptors.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Jul;397(5):1695-704. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-3533-y. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20238109 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Detection of Food Toxins Using Mass Spectrometry.Chem Res Toxicol. 2023 Dec 18;36(12):1834-1863. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00241. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Chem Res Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38059476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Diversity and Anatoxin Profiles of Freshwater Benthic Cyanobacteria From Nova Scotia (Canada).Environ Microbiol. 2025 Mar;27(3):e70067. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.70067. Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40015321 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Methods for Anatoxin-a Determination: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;16(4):198. doi: 10.3390/toxins16040198. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of a multiclass LC-MS/MS method for the analysis of cyanotoxins.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Mar 27. doi: 10.1007/s00216-025-05829-9. Online ahead of print. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40146327
References
-
- Chorus I, Welker M, editors. Toxic cyanobacteria in water. 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (FL), on behalf of the World Health Organization, Geneva. 2021.
-
- World Health Organization . Cyanobacterial toxins: anatoxin-a and analogues. Background document for development of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality and Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Devlin JP, Edwards OE, Gorham PR, Hunter NR, Pike RK, Stavric B. Anatoxin-a, a toxic alkaloid from Anabaena flos-aquae NRC-44h. Can J Chem. 1977;55:1367–1371. doi: 10.1139/v77-189. - DOI
-
- Gorham PR, McLachlan J, Hammer UT, Kim WK. Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. SIL Proc. 2017;15:796–804. doi: 10.1080/03680770.1962.11895606. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

