Non-contrast CT-based radiomics nomogram of pericoronary adipose tissue for predicting haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 37507716
- PMCID: PMC10386261
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-023-01051-0
Non-contrast CT-based radiomics nomogram of pericoronary adipose tissue for predicting haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease than the general population. The aim of this study was to develop a radiomics nomogram of pericoronary adipose tissue (PCAT) based on non-contrast CT to predict haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis in T2DM patients.
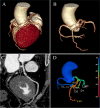
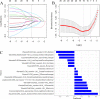
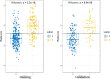
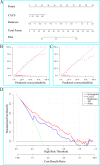
Methods: The study enrolled 215 T2DM patients who underwent non-contrast CT and coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA). CCTA derived fractional flow reserve (FFRCT) ≤ 0.80 was defined as hemodynamically significant stenosis.1691 radiomics features were extracted from PCAT on non-contrast CT. Minimum redundancy maximum relevance (mRMR) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) were used to select useful radiomics features to construct Radscore. Logistic regression was applied to select significant factors among Radscore, fat attenuation index (FAI) and coronary artery calcium score (CACS) to construct radiomics nomogram.
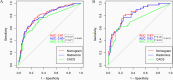
Results: Radscore [odds ratio (OR) = 2.84; P < 0.001] and CACS (OR = 1.00; P = 0.023) were identified as independent predictors to construct the radiomics nomogram. The radiomics nomogram showed excellent performance [training cohort: area under the curve (AUC) = 0.81; 95% CI: 0.76-0.86; validation cohort: AUC = 0.83; 95%CI: 0.76-0.90] to predict haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis in patients with T2DM. Decision curve analysis demonstrated high clinical value of the radiomics nomogram.
Conclusion: The non-contrast CT-based radiomics nomogram of PCAT could effectively predict haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis in patients with T2DM, which might be a potential noninvasive tool for screening of high-risk patients.
Keywords: CCTA derived fractional flow reserve; Haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis; Nomogram; Non-contrast CT; Pericoronary adipose tissue; Radiomics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiomics features of pericoronary adipose tissue improve CT-FFR performance in predicting hemodynamically significant coronary artery stenosis.Eur Radiol. 2023 Mar;33(3):2004-2014. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09175-7. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36258046
-
Identification of patients with acute myocardial infarction based on coronary CT angiography: the value of pericoronary adipose tissue radiomics.Eur Radiol. 2022 Oct;32(10):6868-6877. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08812-5. Epub 2022 May 4. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35505117 Clinical Trial.
-
Predicting haemodynamic significance of coronary stenosis with radiomics-based pericoronary adipose tissue characteristics.Clin Radiol. 2022 Feb;77(2):e154-e161. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2021.10.019. Epub 2021 Nov 28. Clin Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34852918
-
Pericoronary adipose tissue CT attenuation and volume: Diagnostic performance for hemodynamically significant stenosis in patients with suspected coronary artery disease.Eur J Radiol. 2021 Jul;140:109740. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109740. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33971573
-
Incremental diagnostic value of radiomics signature of pericoronary adipose tissue for detecting functional myocardial ischemia: a multicenter study.Eur Radiol. 2023 May;33(5):3007-3019. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09377-z. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36729175
Cited by
-
Serial assessment of coronary artery inflammation using cardiac CT in anthracycline chemotherapy for breast cancer.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul;35(7):3897-3906. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11347-0. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39838089
References
-
- Norhammar A, Malmberg K, Diderholm E, Lagerqvist B, Lindahl B, Rydén L, et al. Diabetes mellitus: the major risk factor in unstable coronary artery disease even after consideration of the extent of coronary artery disease and benefits of revascularization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:585–591. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

