The Radical Scavenging Activities and Anti-Wrinkle Effects of Soymilk Fractions Fermented with Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MK1 and Their Derived Peptides
- PMID: 37507931
- PMCID: PMC10376689
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12071392
The Radical Scavenging Activities and Anti-Wrinkle Effects of Soymilk Fractions Fermented with Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MK1 and Their Derived Peptides
Abstract
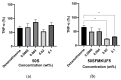
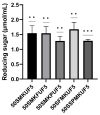
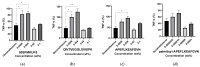
Soybean-derived peptides exert several beneficial effects in various experimental models. However, only a few studies have focused on the radical scavenging and anti-wrinkle effects of soymilk-derived peptides produced via different processes, such as fermentation, enzymatic treatment, and ultrafiltration. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the radical scavenging and antiwrinkle effects of soymilk fractions produced using these processes. We found that 50SFMKUF5, a 5 kDa ultrafiltration fraction fermented with Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MK1 after flavourzyme treatment, exhibited the highest radical scavenging activity using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging assay as well as potent anti-wrinkle effects assessed by type 1 procollagen production and tumor necrosis factor-α production in ultraviolet B (UVB)-treated human dermal fibroblasts and HaCaT keratinocytes. To identify potential bioactive peptides, candidate peptides were synthesized, and their anti-wrinkle effects were assessed. APEFLKEAFGVN (APE), palmitoyl-APE, and QIVTVEGGLSVISPK peptides were synthesized and used to treat UVB-irradiated fibroblasts, HaCaT keratinocytes, and α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced B16F1 melanoma cells. Among these peptides, Pal-APE exerted the strongest effect. Our results highlight the potential of soymilk peptides as anti-aging substances.
Keywords: anti-aging; anti-wrinkle; fermentation; lactic acid bacteria; peptide; radical scavenging activity; soybean milk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
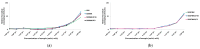
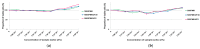
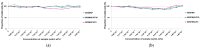

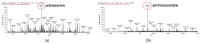


Similar articles
-
Exploring the potential of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei M11 on antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and ACE inhibitory effects of fermented dromedary camel milk (Camelus dromedaries) and the release of antidiabetic and anti-hypertensive peptides.J Food Biochem. 2022 Dec;46(12):e14449. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14449. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36206543
-
Significance of Lactobacillus fermentum on Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities and Ultrafiltration Peptide Fractions as Potential Sources of Antioxidative Peptides from Fermented Camel Milk (Indian Breed).J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Jan;42(1):75-84. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2021.1983485. Epub 2021 Oct 4. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 34605750
-
Antioxidant properties of fermented soymilk and its anti-inflammatory effect on DSS-induced colitis in mice.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 6;9:1088949. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1088949. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36687722 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative activities of soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria.Food Microbiol. 2006 Apr;23(2):128-35. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2005.01.020. Food Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16942996
-
Functional relevance and health benefits of soymilk fermented by lactic acid bacteria.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Jul;133(1):104-119. doi: 10.1111/jam.15342. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34724304 Review.
Cited by
-
Jackfruit Leaf Protein Hydrolysates Obtained by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Leaf Protein Concentrate with Pepsin and Pancreatin: Molecular Weight, Cytotoxicity, Antiproliferative Activity, and Oxidative Stress.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024 Sep;79(3):685-692. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01203-9. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38985367
-
From microbes to molecules: a review of microbial-driven antioxidant peptide generation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 7;40(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03826-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38057638 Review.
-
Phytochemical Profile and Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Cyto-Genotoxic, and Antigenotoxic Potential of Salvia verticillata Hydromethanolic Extract.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;13(5):731. doi: 10.3390/plants13050731. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475577 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Foods and Food Microorganisms: Antioxidant Benefits and Biotechnological Advancements.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 16;13(9):1120. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091120. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qin P., Wang T., Luo Y. A review on plant-based proteins from soybean: Health benefits and soy product development. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022;7:100265. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2021.100265. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

