Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Suggests That Tacrolimus Alters Protection against Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 37507951
- PMCID: PMC10376759
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12071412
Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Suggests That Tacrolimus Alters Protection against Oxidative Stress
Abstract
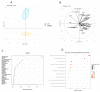
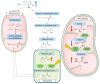
Tacrolimus (FK506) is an immunosuppressant that is experiencing a continuous rise in usage worldwide. The related side effects are known to be globally dose-dependent. Despite numerous studies on FK506, the mechanisms underlying FK506 toxicity are still not well understood. It is therefore essential to explore the toxicity mediated by FK506. To accomplish this, we conducted a targeted metabolomic analysis using LC-MS on the plasma samples of patients undergoing FK506 treatment. The aim was to identify any associated altered metabolic pathway. Another anti-calcineurin immunosuppressive therapy, ciclosporin (CSA), was also studied. Increased plasma concentrations of pipecolic acid (PA) and sarcosine, along with a decrease in the glycine/sarcosine ratio and a tendency of increased plasma lysine was observed in patients under FK506 compared to control samples. Patients under CSA do not show an increase in plasma PA compared to the control samples, which does not support a metabolic link between the calcineurin and PA. The metabolomics changes observed in patients under FK506 highlight a possible link between FK506 and the action of an enzyme involved in both PA and sarcosine catabolism and oxidative pathway, the Peroxisomal sarcosine oxidase (PIPOX). Moreover, PA could be investigated as a potential biomarker of early nephrotoxicity in the follow-up of patients under FK506.
Keywords: immunosuppressive; metabolomics; oxidative stress; pipecolic acid; tacrolimus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targets of immunophilin-immunosuppressant complexes are distinct highly conserved regions of calcineurin A.EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2772-83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07277.x. EMBO J. 1995. PMID: 7540976 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Kaempferol on Tacrolimus-Induced Nephrotoxicity and Calcineurin B1 Expression Level in Animal Model.J Exp Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 28;12:397-407. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S265359. eCollection 2020. J Exp Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33149706 Free PMC article.
-
Nephrotoxicity of cyclosporin A and FK506: inhibition of calcineurin phosphatase.Ren Physiol Biochem. 1995 May-Jun;18(3):128-39. doi: 10.1159/000173910. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1995. PMID: 7542793
-
Nephrotoxicity of immunosuppressive drugs: long-term consequences and challenges for the future.Am J Kidney Dis. 2000 Feb;35(2):333-46. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(00)70348-9. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000. PMID: 10676738 Review.
-
FK506, an immunosuppressant targeting calcineurin function.Curr Med Chem. 2000 Jul;7(7):731-48. doi: 10.2174/0929867003374723. Curr Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 10702636 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress-induced fibrinogen modifications in liver transplant recipients: unraveling a novel potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024 Aug 23;8(6):102555. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102555. eCollection 2024 Aug. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 39309232 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab versus tacrolimus as corticosteroid-sparing therapy for children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized controlled trials.Tzu Chi Med J. 2024 Apr 24;36(3):319-329. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_234_23. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. Tzu Chi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38993828 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

