Exploitation of Quercetin's Antioxidative Properties in Potential Alternative Therapeutic Options for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 37507955
- PMCID: PMC10376113
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12071418
Exploitation of Quercetin's Antioxidative Properties in Potential Alternative Therapeutic Options for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
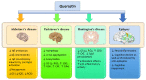
Oxidative stress (OS) is a condition in which there is an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the body, which can lead to cell and tissue damage. This occurs when there is an overproduction of ROS or when the body's antioxidant defense systems are overwhelmed. Quercetin (Que) is part of a group of compounds called flavonoids. It is found in high concentrations in vegetables, fruits, and other foods. Over the past decade, a growing number of studies have highlighted the therapeutic potential of flavonoids to modulate neuronal function and prevent age-related neurodegeneration. Therefore, Que has been shown to have antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties, both in vitro and in vivo. Due to its antioxidant character, Que alleviates oxidative stress, thus improving cognitive function, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. On the other hand, Que can also help support the body's natural antioxidant defense systems, thus being a potentially practical supplement for managing OS. This review focuses on experimental studies supporting the neuroprotective effects of Que in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Huntington's disease (HD), and epilepsy.
Keywords: neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotective effects; oxidative stress; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

