Oxidative Stress: A Suitable Therapeutic Target for Optic Nerve Diseases?
- PMID: 37508003
- PMCID: PMC10376185
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12071465
Oxidative Stress: A Suitable Therapeutic Target for Optic Nerve Diseases?
Abstract
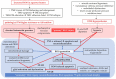
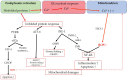
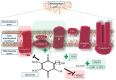
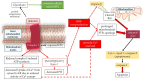
Optic nerve disorders encompass a wide spectrum of conditions characterized by the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and subsequent degeneration of the optic nerve. The etiology of these disorders can vary significantly, but emerging research highlights the crucial role of oxidative stress, an imbalance in the redox status characterized by an excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS), in driving cell death through apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation. This review provides an overview of ROS-related processes underlying four extensively studied optic nerve diseases: glaucoma, Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION), and optic neuritis (ON). Furthermore, we present preclinical findings on antioxidants, with the objective of evaluating the potential therapeutic benefits of targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of optic neuropathies.
Keywords: Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy; glaucoma; ischemic optic neuropathy; optic nerve; optic neuritis; oxidative stress; retinal ganglion cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Van Stavern G.P., Newman N.J. Optic neuropathies. An overview. Ophthalmol. Clin. N. Am. 2001;14 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

