Real-Life Experience of Continuously Infused Ceftolozane/Tazobactam in Patients with Bronchiectasis and Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in the Outpatient Setting
- PMID: 37508309
- PMCID: PMC10376517
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12071214
Real-Life Experience of Continuously Infused Ceftolozane/Tazobactam in Patients with Bronchiectasis and Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in the Outpatient Setting
Abstract
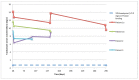
(1) Background: Ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) is a novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor with excellent activity against the multidrug-resistant (MDR) P. aeruginosa. Continuous infusion (CI) dosing allows the optimization of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) properties of β-lactam antibiotics and may support patients' treatment as outpatients. (2) Methods: Adult patients receiving their entire course of C/T as a CI in the outpatient setting were retrospectively included in the study. The primary outcome evaluated was clinical resolution. The secondary outcomes evaluated were PK/PD target attainment (ƒT > 4 × MIC) and microbiologic clearance at the end of treatment. Therapeutic drug monitoring to assess C/T concentration was performed. (3) Results: Three patients were enrolled in the study and received 9 g of C/T in CI every 24 h. One patient received an additional course of antimicrobial therapy due to disease exacerbation six months after initial treatment, accounting for four evaluated treatments. The primary outcome was achieved in 3/4 treatments and the secondary outcome was achieved in 4/4 and 3/3, respectively. In all patients, free ceftolozane concentrations were >10 times higher than the EUCAST breakpoint (4 mg/L). (4) Conclusions: Elastomeric infusion of C/T delivered in CI can be an effective and convenient way to treat acute diseases caused by MDR-P. aeruginosa, avoid hospital admission, and contribute to infection control strategies. Despite the small number of enrolled patients, clinical and microbiological results support this strategy.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; bronchiectasis; ceftolozane/tazobactam; continuous infusion; outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gallagher J.C., Satlin M.J., Elabor A., Saraiya N., McCreary E.K., Molnar E., El-Beyrouty C., Jones B.M., Dixit D., Heil E.L., et al. Ceftolozane-Tazobactam for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections: A Multicenter Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018;5:ofy280. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shortridge D., Castanheira M., Pfaller M.A., Flamm R.K. Ceftolozane-Tazobactam Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from U.S. Hospitals: Report from the PACTS Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 2012 to 2015. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e00465-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00465-17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zerbaxa® (Ceftolozane and Tazobactam) US Prescribing information. Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/206829s011s012....
-
- Zerbaxa® (Ceftolozane and Tazobactam) EMA Summary of Product Characteristics. Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/zerbaxa-epar-....

