Transformer Architecture and Attention Mechanisms in Genome Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 37508462
- PMCID: PMC10376273
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12071033
Transformer Architecture and Attention Mechanisms in Genome Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
The emergence and rapid development of deep learning, specifically transformer-based architectures and attention mechanisms, have had transformative implications across several domains, including bioinformatics and genome data analysis. The analogous nature of genome sequences to language texts has enabled the application of techniques that have exhibited success in fields ranging from natural language processing to genomic data. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the most recent advancements in the application of transformer architectures and attention mechanisms to genome and transcriptome data. The focus of this review is on the critical evaluation of these techniques, discussing their advantages and limitations in the context of genome data analysis. With the swift pace of development in deep learning methodologies, it becomes vital to continually assess and reflect on the current standing and future direction of the research. Therefore, this review aims to serve as a timely resource for both seasoned researchers and newcomers, offering a panoramic view of the recent advancements and elucidating the state-of-the-art applications in the field. Furthermore, this review paper serves to highlight potential areas of future investigation by critically evaluating studies from 2019 to 2023, thereby acting as a stepping-stone for further research endeavors.
Keywords: attention mechanism; bioinformatics; deep learning; genome data; genomics; natural language processing; sequence analysis; transcriptome data; transformer model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim no conflict of interest.
Figures
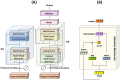
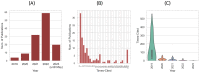
Similar articles
-
Leveraging transformers-based language models in proteome bioinformatics.Proteomics. 2023 Dec;23(23-24):e2300011. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300011. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37381841 Review.
-
Applications of transformer-based language models in bioinformatics: a survey.Bioinform Adv. 2023 Jan 11;3(1):vbad001. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbad001. eCollection 2023. Bioinform Adv. 2023. PMID: 36845200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do it the transformer way: A comprehensive review of brain and vision transformers for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis and classification.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Dec;167:107667. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107667. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37939407 Review.
-
Extending Protein Language Models to a Viral Genomic Scale Using Biologically Induced Sparse Attention.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 11:2025.05.29.656907. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.29.656907. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501585 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Nucleic Transformer: Classifying DNA Sequences with Self-Attention and Convolutions.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Nov 17;12(11):3205-3214. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00154. Epub 2023 Nov 2. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37916871 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advanced feature fusion of radiomics and deep learning for accurate detection of wrist fractures on X-ray images.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 20;26(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08733-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40394557 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities, challenges and future perspectives of using bioinformatics and artificial intelligence techniques on tropical disease identification using omics data.Front Digit Health. 2024 Nov 25;6:1471200. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1471200. eCollection 2024. Front Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39654982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CalTrig: A GUI-Based Machine Learning Approach for Decoding Neuronal Calcium Transients in Freely Moving Rodents.eNeuro. 2025 Jul 15;12(7):ENEURO.0009-25.2025. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0009-25.2025. Print 2025 Jul. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 40603011 Free PMC article.
-
A review of transformer models in drug discovery and beyond.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Jun;15(6):101081. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101081. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40635975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CalTrig: A GUI-based Machine Learning Approach for Decoding Neuronal Calcium Transients in Freely Moving Rodents.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 19:2024.09.30.615860. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.30.615860. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: eNeuro. 2025 Jul 15;12(7):ENEURO.0009-25.2025. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0009-25.2025. PMID: 39372793 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

