Mental Health and Psychosocial Problems among Children and Adolescents in Jordan: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 37508662
- PMCID: PMC10377849
- DOI: 10.3390/children10071165
Mental Health and Psychosocial Problems among Children and Adolescents in Jordan: A Scoping Review
Abstract
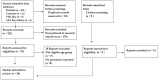
Introduction: In Jordan, mental health morbidity among children and adolescents is on the rise. Several studies in Jordan have assessed mental health issues and their associated factors among adolescents; however, there remains a lack of a collation of data regarding such issues. Objectives: To review the prevalence rates of mental health problems among children and adolescents in Jordan to understand the evidence base concerning psychiatric morbidity. Methods: The PubMed database, Cochrane Library, Virtual Health Library (VHL) Lilac, and APA PsycArticles were searched for literature published between January 2010 and May 2023. Studies were included if they were conducted on children and adolescents (≤19 years), were observational studies that reported prevalence data regarding psychosocial problems, and were studies conducted in Jordan. Results: The search yielded 211 records, of which 33 studies were assessed for eligibility and 28 met the inclusion criteria. The sample age ranged from 6-19 years. The prevalence rates ranged from 7.1% to 73.8% for depression, 16.3% to 46.8% for anxiety, 13.0-40.6% for ADHD, 11.7-55.2% for overall emotional and behavioral difficulties, 16.2-65.1% for PTSD, and 12-40.4% for eating disorders. Conclusions: The findings highlight the magnitude of mental health problems among children and adolescents and the heterogeneity of the results. Further studies are needed to investigate the prevalence of eating disorders among refugees, as well as sleeping disorders and substance use disorders among all adolescents.
Keywords: children and adolescents; mental health; mental health disorders; psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Piao J., Huang Y., Han C., Li Y., Xu Y., Liu Y., He X. Alarming Changes in the Global Burden of Mental Disorders in Children and Adolescents from 1990 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2022;31:1827–1845. doi: 10.1007/s00787-022-02040-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- UNICEF Adolescent Health Dashboards. [(accessed on 23 September 2022)]. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/resources/adolescent-health-dashboards-country-p...
-
- Vos T., Lim S.S., Abbafati C., Abbas K.M., Abbasi M., Abbasifard M., Abbasi-Kangevari M., Abbastabar K., Abd-Allah F., Bhutta Z.A., et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396:1204–1222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Mazidi M., Li K., Li Y., Chen S., Kirwan R., Zhou H., Yan N., Rahman A., Wang W., et al. Prevalence of Mental Health Problems among Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021;293:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.06.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNHCR Jordan Factsheet. [(accessed on 25 September 2022)]. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/jordan/unhcr-jordan-factsheet-may-2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous