Performance Comparison of Object Detection Networks for Shrapnel Identification in Ultrasound Images
- PMID: 37508834
- PMCID: PMC10376403
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10070807
Performance Comparison of Object Detection Networks for Shrapnel Identification in Ultrasound Images
Abstract
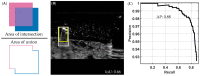
Ultrasound imaging is a critical tool for triaging and diagnosing subjects but only if images can be properly interpreted. Unfortunately, in remote or military medicine situations, the expertise to interpret images can be lacking. Machine-learning image interpretation models that are explainable to the end user and deployable in real time with ultrasound equipment have the potential to solve this problem. We have previously shown how a YOLOv3 (You Only Look Once) object detection algorithm can be used for tracking shrapnel, artery, vein, and nerve fiber bundle features in a tissue phantom. However, real-time implementation of an object detection model requires optimizing model inference time. Here, we compare the performance of five different object detection deep-learning models with varying architectures and trainable parameters to determine which model is most suitable for this shrapnel-tracking ultrasound image application. We used a dataset of more than 16,000 ultrasound images from gelatin tissue phantoms containing artery, vein, nerve fiber, and shrapnel features for training and evaluating each model. Every object detection model surpassed 0.85 mean average precision except for the detection transformer model. Overall, the YOLOv7tiny model had the higher mean average precision and quickest inference time, making it the obvious model choice for this ultrasound imaging application. Other object detection models were overfitting the data as was determined by lower testing performance compared with higher training performance. In summary, the YOLOv7tiny object detection model had the best mean average precision and inference time and was selected as optimal for this application. Next steps will implement this object detection algorithm for real-time applications, an important next step in translating AI models for emergency and military medicine.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; image interpretation; machine learning; neurovascular; object detection; shrapnel; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
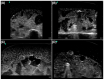
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using AI Segmentation Models to Improve Foreign Body Detection and Triage from Ultrasound Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 29;11(2):128. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020128. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391614 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of an Object Detection Algorithm for Shrapnel and Development of a Triage Tool to Determine Injury Severity.J Imaging. 2022 Sep 19;8(9):252. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8090252. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36135417 Free PMC article.
-
Using an Ultrasound Tissue Phantom Model for Hybrid Training of Deep Learning Models for Shrapnel Detection.J Imaging. 2022 Oct 2;8(10):270. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8100270. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36286364 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Automatic Assisted Detection of Uterine Fibroid in Ultrasound Images Using a Deep Learning Detector.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023 Jul;49(7):1616-1626. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2023.03.013. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37121880 Review.
-
A comprehensive review of methods based on deep learning for diabetes-related foot ulcers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 8;13:945020. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.945020. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36004341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence in Advanced Medical Imaging.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Dec 5;11(12):1229. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11121229. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768047 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Image Analysis with Vision Transformers-Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;14(5):542. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050542. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using AI Segmentation Models to Improve Foreign Body Detection and Triage from Ultrasound Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 29;11(2):128. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020128. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gil-Rodríguez J., Pérez de Rojas J., Aranda-Laserna P., Benavente-Fernández A., Martos-Ruiz M., Peregrina-Rivas J.-A., Guirao-Arrabal E. Ultrasound Findings of Lung Ultrasonography in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022;148:110156. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110156. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

