Exoscopic Microsurgery: A Change of Paradigm in Brain Tumor Surgery? Comparison with Standard Operative Microscope
- PMID: 37508967
- PMCID: PMC10377370
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13071035
Exoscopic Microsurgery: A Change of Paradigm in Brain Tumor Surgery? Comparison with Standard Operative Microscope
Abstract
Background: The exoscope is a high-definition telescope recently introduced in neurosurgery. In the past few years, several reports have described the advantages and disadvantages of such technology. No studies have compared results of surgery with standard microscope and exoscope in patients with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
Methods: Our retrospective study encompassed 177 patients operated on for GBM (WHO 2021) between February 2017 and August 2022. A total of 144 patients were operated on with a microscope only and the others with a 3D4K exoscope only. All clinical and radiological data were collected. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) have been estimated in the two groups and compared by the Cox model adjusting for potential confounders (e.g., sex, age, Karnofsky performance status, gross total resection, MGMT methylated promoter, and operator's experience).
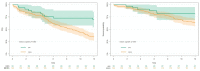
Results: IDH was mutated in 9 (5.2%) patients and MGMT was methylated in 76 (44.4%). Overall, 122 patients received a gross total resection, 14 patients received a subtotal resection, and 41 patients received a partial resection. During follow-up, 139 (73.5%) patients experienced tumor recurrence and 18.7% of them received a second surgery. After truncation to 12 months, the median PFS for patients operated on with the microscope was 8.82 months, while for patients operated on with the exoscope it was >12 months. Instead, the OS was comparable in the two groups. The multivariable Cox model showed that the use of microscope compared to the exoscope was associated with lower progression-free survival (hazard ratio = 3.55, 95%CI = 1.66-7.56, p = 0.001).
Conclusions: The exoscope has proven efficacy in terms of surgical resection, which was not different to that of the microscope. Furthermore, patients operated on with the exoscope had a longer PFS. A comparable OS was observed between microscope and exoscope, but further prospective studies with longer follow-up are needed.
Keywords: brain tumors; en bloc resection; exoscope; extent of resection; glioblastoma; neurosurgery; operative microscope; perilesional resection; progression-free survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed S.I., Javed G., Mubeen B., Bareeqa S.B., Rasheed H., Rehman A., Phulpoto M.M., Samar S.S., Aziz K. Robotics in neurosurgery: A literature review. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018;68:258–263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

