Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) and Pulmonary Involvement in COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 37509076
- PMCID: PMC10377146
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13071040
Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) and Pulmonary Involvement in COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
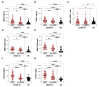
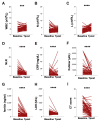
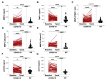
Background: The aim of the study was to longitudinally evaluate the association between MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and chest radiological findings in COVID-19 patients. Methods: COVID-19 patients were evaluated based on their hospital admission (baseline) and three months after hospital discharge (T post) and were stratified into ARDS and non-ARDS groups. As a control group, healthy donors (HD) were enrolled. Results: At the baseline, compared to HD (n = 53), COVID-19 patients (n = 129) showed higher plasma levels of MMP-9 (p < 0.0001) and TIMP-1 (p < 0.0001) and the higher plasma activity of MMP-2 (p < 0.0001) and MMP-9 (p < 0.0001). In the ARDS group, higher plasma levels of MMP-9 (p = 0.0339) and TIMP-1 (p = 0.0044) and the plasma activity of MMP-2 (p = 0.0258) and MMP-9 (p = 0.0021) compared to non-ARDS was observed. A positive correlation between the plasma levels of TIMP-1 and chest computed tomography (CT) score (ρ = 0.2302, p = 0.0160) was observed. At the T post, a reduction in plasma levels of TIMP-1 (p < 0.0001), whereas an increase in the plasma levels of MMP-9 was observed (p = 0.0088). Conclusions: The positive correlation between TIMP-1 with chest CT scores highlights its potential use as a marker of fibrotic burden. At T post, the increase in plasma levels of MMP-9 and the reduction in plasma levels of TIMP-1 suggested that inflammation and fibrosis resolution were still ongoing.
Keywords: ELISA; MMP-2; MMP-9; PASC; computed tomography; matrix metalloproteinases; post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection; pulmonary fibrosis; sCD14; sCD163; zymography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Zingaropoli M.A., Perri V., Pasculli P., Cogliati Dezza F., Nijhawan P., Savelloni G., La Torre G., D’Agostino C., Mengoni F., Lichtner M., et al. Major Reduction of NKT Cells in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. Clin. Immunol. 2021;222:108630. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108630. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

