The Development and Role of Capmatinib in the Treatment of MET-Dysregulated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37509224
- PMCID: PMC10377299
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15143561
The Development and Role of Capmatinib in the Treatment of MET-Dysregulated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-A Narrative Review
Abstract
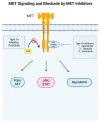
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a leading cause of death, but over the past decade, there has been tremendous progress in the field with new targeted therapies. The mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET) proto-oncogene has been implicated in multiple solid tumors, including NSCLC, and dysregulation in NSCLC from MET can present most notably as MET exon 14 skipping mutation and amplification. From this, MET tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been developed to treat this dysregulation despite challenges with efficacy and reliable biomarkers. Capmatinib is a Type Ib MET TKI first discovered in 2011 and was FDA approved in August 2022 for advanced NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutation. In this narrative review, we discuss preclinical and early-phase studies that led to the GEOMETRY mono-1 study, which showed beneficial efficacy in MET exon 14 skipping mutations, leading to FDA approval of capmatinib along with Foundation One CDx assay as its companion diagnostic assay. Current and future directions of capmatinib are focused on improving the efficacy, overcoming the resistance of capmatinib, and finding approaches for new indications of capmatinib such as acquired MET amplification from epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) TKI resistance. Clinical trials now involve combination therapy with capmatinib, including amivantamab, trametinib, and immunotherapy. Furthermore, new drug agents, particularly antibody-drug conjugates, are being developed to help treat patients with acquired resistance from capmatinib and other TKIs.
Keywords: MET dysregulation; NSCLC; capmatinib; detection; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
RH is a consultant for Targeted Oncology and received honoraria from DAVA Oncology and The Dedham Group. D.J.B. has received consulting fees from Seagen. MN has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Caris Life Sciences, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Lilly and Genentech, has received travel support from AnHeart Therapeutics and is a speaker for Takeda, Janssen, Mirati and Blueprint Medicines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Capmatinib for patients with non-small cell lung cancer with MET exon 14 skipping mutations: A review of preclinical and clinical studies.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Apr;95:102173. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102173. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 33740553 Review.
-
Targeted Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Capmatinib with Companion Diagnostics.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Nov 23;14:5321-5331. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S273357. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34853516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Trial Report: A Multicenter Phase I/Ib study of Capmatinib Plus Trametinib in Patients With Metastatic Nonsmall Cell Lung Center Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations and Other MET-Alterations.Clin Lung Cancer. 2024 Dec;25(8):732-737. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2024.07.002. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Clin Lung Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39089913 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Ib/II Study of Capmatinib (INC280) Plus Gefitinib After Failure of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitor Therapy in Patients With EGFR-Mutated, MET Factor-Dysregulated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2018 Nov 1;36(31):3101-3109. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7326. Epub 2018 Aug 29. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30156984 Clinical Trial.
-
Capmatinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019 Aug;19(8):659-671. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1643239. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31368815 Review.
Cited by
-
Real world experience with MET inhibitors in MET exon 14 skipping mutated non-small cell lung cancer: largest Indian perspective.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 8;16(1):286. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01864-1. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40056282 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting c-Met in Cancer Therapy: Unravelling Structure-activity Relationships and Docking Insights for Enhanced Anticancer Drug Design.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(4):409-433. doi: 10.2174/0115680266331025241015084546. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39484763 Review.
-
A real-world pharmacovigilance study of FDA adverse event reporting system events for Capmatinib.Sci Rep. 2024 May 18;14(1):11388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62356-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38762672 Free PMC article.
-
The Different Roles of MET in the Development and Treatment of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 21;15(20):5087. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205087. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894454 Free PMC article.
-
Mining and evaluation of adverse event signals for capmatinib based on the FAERS database.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1417661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1417661. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39380910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Planchard D., Smit E.F., Groen H.J.M., Mazieres J., Besse B., Helland Å., Giannone V., D’Amelio A.M., Zhang P., Mookerjee B., et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1307–1316. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30679-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaw A.T., Riely G.J., Bang Y.-J., Kim D.-W., Camidge D.R., Solomon B.J., Varella-Garcia M., Iafrate A.J., Shapiro G.I., Usari T., et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-rearranged advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Updated results, including overall survival, from PROFILE 1001. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1121–1126. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz131. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drilon A., Siena S., Dziadziuszko R., Barlesi F., Krebs M.G., Shaw A.T., de Braud F., Rolfo C., Ahn M.-J., Wolf J., et al. Entrectinib in ROS1 fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:261–270. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30690-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

