Diabetes Mellitus in Pancreatic Cancer: A Distinct Approach to Older Subjects with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 37509329
- PMCID: PMC10377806
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15143669
Diabetes Mellitus in Pancreatic Cancer: A Distinct Approach to Older Subjects with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is associated with a very poor prognosis, with near-identical incidence and mortality. According to the World Health Organization Globocan Database, the estimated number of new cases worldwide will rise by 70% between 2020 and 2040. There are no effective screening methods available so far, even for high-risk individuals. The prognosis of PDAC, even at its early stages, is still mostly unsatisfactory. Impaired glucose metabolism is present in about 3/4 of PDAC cases.
Methods: Available literature on pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus was reviewed using a PubMed database. Data from a national oncology registry (on PDAC) and information from a registry of healthcare providers (on diabetes mellitus and a number of abdominal ultrasound investigations) were obtained.
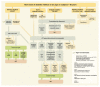
Results: New-onset diabetes mellitus in subjects older than 60 years should be an incentive for a prompt and detailed investigation to exclude PDAC. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, diabetes mellitus associated with chronic non-malignant diseases of the exocrine pancreas, and PDAC-associated type 3c diabetes mellitus are the most frequent types. Proper differentiation of particular types of new-onset diabetes mellitus is a starting point for a population-based program. An algorithm for subsequent steps of the workup was proposed.
Conclusions: The structured, well-differentiated, and elaborately designed approach to the elderly with a new onset of diabetes mellitus could improve the current situation in diagnostics and subsequent poor outcomes of therapy of PDAC.
Keywords: age over 60 years; diagnostic algorithm; new-onset diabetes mellitus; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the manuscript; in the collection and interpretation of own and literature data; in the concept of a distinct approach to older subjects with new-onset diabetes mellitus; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish it.
Figures
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. 2023. [(accessed on 9 April 2023)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

