Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor for the Early Detection of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Recurrences: Could Cystoscopy Be Substituted?
- PMID: 37509344
- PMCID: PMC10378094
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15143683
Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor for the Early Detection of Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Recurrences: Could Cystoscopy Be Substituted?
Abstract
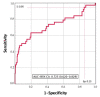
XBM was prospectively assessed in spontaneous urine collected just before flexible cystoscopy and washing cytology carried out within the first 2 years follow-up of 337 patients with NMIBC. Recurrences were pathologically confirmed in 49 patients (14.5%), 22 of them being high-risk (6.5%). The XBM sensitivity for detecting any type of recurrence was 69.4% and 63.6% in the cases of high-risk NMIBC. Negative predictive value (NPV) for XBM was 93% for all recurrences and 96.2% for high-risk recurrences. XBM could have avoided 213 invasive controls but missed the detection of 15 recurrences (30.6%)-8 of them of high-risk (36.4%). XBM false positive elevations were detected in 90 patients (26.7%), whereas 10 patients with the invasive method had a false positive result (3%), p <0.001. However, early detection of recurrences during the first year's follow-up after an XBM false positive result was observed in 18 patients (20%). On the other hand, 19 recurrences were detected during this period among the rest of the patients (7.7%)-p = 0.003, and odds ratio (OR) 3.0 (95% CI 1.5-6.0). Regarding one-year follow-up recurrences, 10% were high-risk recurrences in the XBM false positive group and 3.2% in the rest of the patients-p = 0.021, and OR 3.3 (95% CI 1.2-8.9). Additionally, 11.3% of the patients without false positive results developed a recurrence, p = 0.897, for any recurrence, being 10% and 5.2%, respectively, and high-risk and low-risk recurrences, p = 0.506. After searching for the best XBM cutoff for detecting the 38 high-risk initial recurrences and the early high-risk recurrences after a one-year follow-up, a linear discriminant analysis (LDA) of 0.13 could have avoided 11.3% of cystoscopies and bladder wash cytologies, as this cutoff missed only 1 high-risk recurrence (2.6%). More extensive and well-designed studies will confirm if XBM can improve the surveillance of NMIBC.
Keywords: biomarker; bladder cancer; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article do not declare any conflict of interest. Cepheid had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal follow-up and performance validation of an mRNA-based urine test (Xpert® Bladder Cancer Monitor ) for surveillance in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.BJU Int. 2021 Dec;128(6):713-721. doi: 10.1111/bju.15418. Epub 2021 May 5. BJU Int. 2021. PMID: 33793062 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Validation of Clinical Usefulness of a Novel mRNA-based Urine Test (Xpert® Bladder Cancer Monitor) for surveillance in Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer.Urol Oncol. 2021 Jan;39(1):77.e9-77.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.07.013. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32800441
-
Clinical performance of Xpert Bladder Cancer (BC) Monitor, a mRNA-based urine test, in active surveillance (AS) patients with recurrent non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC): results from the Bladder Cancer Italian Active Surveillance (BIAS) project.World J Urol. 2020 Sep;38(9):2215-2220. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-03002-3. Epub 2019 Nov 5. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31691083
-
Follow-up in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer-International Bladder Cancer Network recommendations.Urol Oncol. 2016 Oct;34(10):460-8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.028. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27368880 Review.
-
Novel urinary biomarkers ADXBLADDER and bladder EpiCheck for diagnostics of bladder cancer: A review.Urol Oncol. 2021 Mar;39(3):161-170. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.11.014. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33376063 Review.
Cited by
-
Unleashing the power of urine‑based biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and monitoring of bladder cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Mar;66(3):18. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5724. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39917986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic performance of advanced large language models in cystoscopy: evidence from a retrospective study and clinical cases.BMC Urol. 2025 Mar 29;25(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12894-025-01740-8. BMC Urol. 2025. PMID: 40158093 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

