Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37509467
- PMCID: PMC10376908
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071827
Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) Are Superior to Anti-PD-L1 mAbs When Combined with Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (mNSCLC): A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
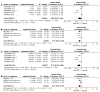
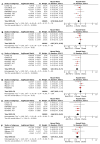
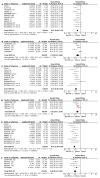
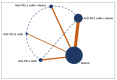
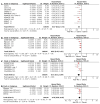
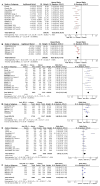
Platinum-based chemotherapy combined with anti-PD-1 or PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is now standard first-line therapy for mNSCLC patients without sensitizing driver mutations. Anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 mAbs are considered to be equivalent in efficacy. In the absence of head-to-head randomized control trials (RCTs), we utilized network meta-analysis (NWM) to provide an indirect comparison of their efficacy. A systematic literature review and NWM were performed using RCTs that investigated anti-PD-1 or PD-L1 mAbs ± chemotherapy in patients with mNSCLC in the first-line setting. The primary outcome was comparative overall survival (OS), while secondary outcomes were comparative progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and rate of grade 3 and higher toxicities. We identified 24 RCTs. Patients treated with anti-PD-1 mAb + chemotherapy compared with anti-PD-L1 mAb + chemotherapy showed superior mOS, mPFS, and ORR with a similar rate of grade 3 and higher toxicities. This difference in mOS was most pronounced in the PD-L1 TPS 1-49% population. The two mAbs were equivalent as single agents. Anti-PD-1 mAb + chemotherapy improved mOS when compared to anti-PD-1 mAb monotherapy, whereas anti-PD-L1 mAbs + chemotherapy did not when compared to anti-PD-L1 mAb monotherapy. Head-to-head RCTs are warranted in the future.
Keywords: anti-PD-1; anti-PD-L1; chemoimmunotherapy; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Motzer R.J., Tannir N.M., McDermott D.F., Arén Frontera O., Melichar B., Choueiri T.K., Plimack E.R., Barthélémy P., Porta C., George S., et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:1277–1290. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1712126. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

