HLA-DR Expression on Monocytes and Sepsis Index Are Useful in Predicting Sepsis
- PMID: 37509475
- PMCID: PMC10377223
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071836
HLA-DR Expression on Monocytes and Sepsis Index Are Useful in Predicting Sepsis
Abstract
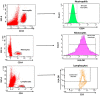
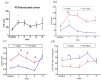
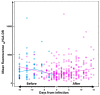
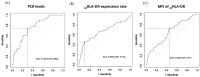
The reduction of mortality in patients with sepsis depends on the early identification and treatment of at-risk patients. The aim was to evaluate the HLA-DR expression on the surface of monocytes (MHLA-DR ratio), the sepsis index (CD64 expression on neutrophils/MHLA-DR ratio), and C-reactive protein (CRP) with the development of sepsis. We prospectively enrolled 77 critically ill patients, 59 with stroke and 18 with traumatic brain injuries. The biomarkers were tested at the baseline and 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 days later. Most patients (71%) developed sepsis (4.2 ± 1.3 days after admission). On day 3, those subsequently developing sepsis had lower levels of MHLA-DR+ (81.7 ± 16.2% vs. 88.5 ± 12.1%, p < 0.05) and higher sepsis indexes (0.19 ± 0.19 vs. 0.08 ± 0.08, p < 0.01) than those not developing sepsis. The MHLA-DR ratio slowly recovered before day 6, while the sepsis index remained raised in septic patients up to day 9 (p < 0.05). To predict the development of sepsis, optimal cut-offs were CRP levels > 106.90 mg/mL (74.19% sensitivity, 69.49 specificity) and MHLA-DR expression rate < 72.80% (45.31% sensitivity, 89.47% specificity). The periodic monitoring of the MHLA-DR expression together with CRP and sepsis index may help to identify patients in the ICU at increased risk of developing sepsis.
Keywords: biomarker; sepsis; sepsis index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jones S.L., Ashton C.M., Kiehne L., Gigliotti E., Bell-Gordon C., Disbot M., Masud F., Shirkey B.A., Wray N.P. Reductions in Sepsis Mortality and Costs After Design and Implementation of a Nurse-Based Early Recognition and Response Program. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 2015;41:483–491. doi: 10.1016/S1553-7250(15)41063-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damiani E., Donati A., Serafini G., Rinaldi L., Adrario E., Pelaia P., Busani S., Girardis M. Effect of performance improvement programs on compliance with sepsis bundles and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0125827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125827. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

