ERK Signaling Pathway Is Constitutively Active in NT2D1 Non-Seminoma Cells and Its Inhibition Impairs Basal and HGF-Activated Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 37509533
- PMCID: PMC10377482
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071894
ERK Signaling Pathway Is Constitutively Active in NT2D1 Non-Seminoma Cells and Its Inhibition Impairs Basal and HGF-Activated Cell Proliferation
Abstract
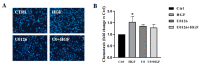
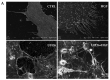
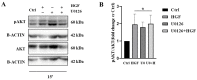
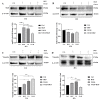
c-MET/hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) system deregulation is a well-known feature of malignancy in several solid tumors, and for this reason this system and its pathway have been considered as potential targets for therapeutic purposes. In previous manuscripts we reported c-MET/HGF expression and the role in testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) derived cell lines. We demonstrated the key role of c-Src and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT adaptors in the HGF-dependent malignant behavior of the embryonal carcinoma cell line NT2D1, finding that the inhibition of these onco-adaptor proteins abrogates HGF triggered responses such as proliferation, migration, and invasion. Expanding on these previous studies, herein we investigated the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) pathways in the HGF-dependent and HGF-independent NT2D1 cells biological responses. To inhibit MAPK/ERK pathways we chose a pharmacological approach, by using U0126 inhibitor, and we analyzed cell proliferation, collective migration, and chemotaxis. The administration of U0126 together with HGF reverts the HGF-dependent activation of cell proliferation but, surprisingly, does not exert the same effect on NT2D1 cell migration. In addition, we found that the use of U0126 alone significantly promotes the acquisition of NT2D1 «migrating phenotype», while collective migration of NT2D1 cells was stimulated. Notably, the inhibition of ERK activation in the absence of HGF stimulation resulted in the activation of the AKT-mediated pathway, and this let us speculate that the paradoxical effects obtained by using U0126, which are the increase of collective migration and the acquisition of partial epithelium-mesenchyme transition (pEMT), are the result of compensatory pathways activation. These data highlight how the specific response to pathway inhibitors, should be investigated in depth before setting up therapy.
Keywords: MAPK/ERK pathway; c-Met/HGF system; testicular germ cell tumors; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Huang X., Chen Z., Zhang N., Zhu C., Lin X., Yu J., Chen Z., Lan P., Wan Y. Increase in CD4+FOXP3+ regulatory T cell number and upregulation of the HGF/c-Met signaling pathway during the liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020;20:2113–2118. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11785. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scheri K.C., Leonetti E., Laino L., Gigantino V., Gesualdi L., Grammatico P., Bizzarri M., Franco R., Oosterhuis J.W., Stoop H., et al. c-MET receptor as potential biomarker and target molecule for malignant testicular germ cell tumors. Oncotarget. 2018;9:31842–31860. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gesualdi L., Leonetti E., Cucina A., Scicchitano B.M., Sorrentino S., Tarsitano M.G., Isidori A., Bizzarri M., Filippini A., Riccioli A., et al. The PI3K/AKT Pathway Is Activated by HGF in NT2D1 Non-Seminoma Cells and Has a Role in the Modulation of Their Malignant Behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:8669. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228669. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

