Role of Macrophage lncRNAs in Mediating Inflammatory Processes in Atherosclerosis and Sepsis
- PMID: 37509544
- PMCID: PMC10377468
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071905
Role of Macrophage lncRNAs in Mediating Inflammatory Processes in Atherosclerosis and Sepsis
Abstract
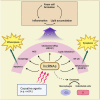
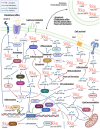
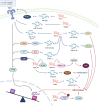
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are molecules >200 bases in length without protein-coding functions implicated in signal transduction and gene expression regulation via interaction with proteins or RNAs, exhibiting various functions. The expression of lncRNAs has been detected in many cell types, including macrophages, a type of immune cell involved in acute and chronic inflammation, removal of dead or damaged cells, and tissue repair. Increasing evidence indicates that lncRNAs play essential roles in macrophage functions and disease development. Additionally, many animal studies have reported that blockage or modulation of lncRNA functions alleviates disease severity or morbidity rate. The present review summarizes the current knowledge regarding lncRNAs expressed in macrophages, focusing on their molecular targets and the biological processes regulated by them during the development of inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis and sepsis. Possible application of this information to lncRNA-targeting therapy is also discussed. The studies regarding macrophage lncRNAs described in this review can help provide valuable information for developing treatments for various pathological conditions involving macrophages.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; inflammation; lncRNA; macrophage; sepsis; therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

