Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Based Delivery of Macromolecular Drugs: Development, Strategies, and Progress
- PMID: 37509610
- PMCID: PMC10377493
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11071971
Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Based Delivery of Macromolecular Drugs: Development, Strategies, and Progress
Abstract
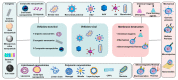
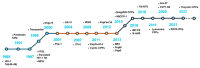
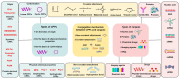
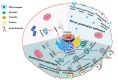
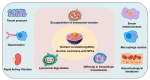
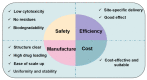
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), developed for more than 30 years, are still being extensively studied due to their excellent delivery performance. Compared with other delivery vehicles, CPPs hold promise for delivering different types of drugs. Here, we review the development process of CPPs and summarize the composition and classification of the CPP-based delivery systems, cellular uptake mechanisms, influencing factors, and biological barriers. We also summarize the optimization routes of CPP-based macromolecular drug delivery from stability and targeting perspectives. Strategies for enhanced endosomal escape, which prolong its half-life in blood, improved targeting efficiency and stimuli-responsive design are comprehensively summarized for CPP-based macromolecule delivery. Finally, after concluding the clinical trials of CPP-based drug delivery systems, we extracted the necessary conditions for a successful CPP-based delivery system. This review provides the latest framework for the CPP-based delivery of macromolecular drugs and summarizes the optimized strategies to improve delivery efficiency.
Keywords: biological barrier; cell-penetrating peptide; cellular uptake mechanism; macromolecular drug delivery; optimized strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent Advances of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Their Application as Vectors for Delivery of Peptide and Protein-Based Cargo Molecules.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 7;15(8):2093. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082093. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Penetrating Peptides: A Powerful Tool for Targeted Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Deliv. 2024;21(3):368-388. doi: 10.2174/1567201820666230407092924. Curr Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 37026498 Review.
-
Recent in vivo advances in cell-penetrating peptide-assisted drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(3):373-87. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2016.1125879. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26634750 Review.
-
Overcoming the cellular barriers and beyond: Recent progress on cell penetrating peptide modified nanomedicine in combating physiological and pathological barriers.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jul;17(4):523-543. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.05.002. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36105313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the Impact of Payload Conjugation on the Cell-Penetrating Efficiency of the Endosomal Escape Peptide dfTAT: Implications for Future Designs for CPP-Based Delivery Systems.Bioconjug Chem. 2023 Oct 18;34(10):1861-1872. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00369. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Bioconjug Chem. 2023. PMID: 37774419 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cell-penetrating peptides for sustainable agriculture.Trends Plant Sci. 2024 Oct;29(10):1131-1144. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2024.05.011. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Trends Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38902122 Review.
-
Research progress and strategies for the biosynthesis of keratinocyte growth factor-2 (KGF-2) in Arabidopsis thaliana.PeerJ. 2025 May 27;13:e19440. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19440. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40452924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feature Collection in Peptide Therapeutics: Current Applications and Future Directions.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 23;12(12):2919. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122919. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767825 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Screening of Peptide Libraries: The Search for Peptide-Based Therapeutics Using Computational Tools.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1798. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031798. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cell-Penetrating Peptide Improves Anti-HER2 Single-Chain Variable Fragment Internalization and Antitumor Activity against HER2-Positive Breast Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo.Molecules. 2024 Mar 11;29(6):1247. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061247. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38542884 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- F1034361/National Translational Science Center for Molecular Medicine Fund
- CPAYLJ202003/Chinese Pharmacertical Association-Yiling Pharmacertical Innovation Fund
- XB202010/Key Research Fund of Tianjin Project & Team
- 20YFZCSY00450/Key Research and Development Program of Tianjin
- 21JCZDJC00230/Key Program of Natural Science Fund of Tianjin
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

