Efficacy of Power Ultrasound-Based Hurdle Technology on the Reduction of Bacterial Pathogens on Fresh Produce
- PMID: 37509745
- PMCID: PMC10378333
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12142653
Efficacy of Power Ultrasound-Based Hurdle Technology on the Reduction of Bacterial Pathogens on Fresh Produce
Abstract
Minimally processed produce is frequently contaminated with foodborne bacterial pathogens. Power ultrasound is a non-thermal and cost-effective technology that can be combined with other chemical sanitization methods. This study investigated the reduction of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Newport on grape tomato, romaine lettuce, and spinach washed with water, chlorine, or peroxyacetic acid alone or in combination with 25 or 40 kHz power ultrasound for 1, 2, or 5 min. Produce items were inoculated with either pathogen at 10 log CFU/g, dried for 2 h, and treated. Combined treatment of ultrasound and sanitizers resulted in 1.44-3.99 log CFU/g reduction of L. monocytogenes and 1.35-3.62 log CFU/g reduction of S. Newport, with significantly higher reductions observed on grape tomato. Synergistic effects were achieved with the hurdle treatment of power ultrasound coupled with the chemical sanitizers when compared to the single treatments; an additional 0.48-1.40 log CFU/g reduction of S. Newport was obtained with the addition of power ultrasound on grape tomato. In general, no significant differences were observed in pathogen reductions between the ultrasound frequencies, the sanitizers, or the treatment lengths. Results from this study suggest that incorporation of power ultrasound into the current washing procedure may be beneficial for the reduction, but not elimination, of bacterial pathogens on certain produce items, including tomatoes.
Keywords: L. monocytogenes; S. Newport; chemical sanitizers; fresh produce; hurdle technology; power ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





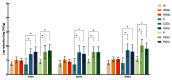
References
-
- Roerink A.-M. 2021 Surpasses 2020 in Dollars but Volume Was not Able to Hold the Line. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.freshproduce.com/resources/retail/iri-reports/2021-surpasses...
-
- CDC Listeria Outbreaks. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/outbreaks/index.html.
-
- CDC National Outbreak Reporting System (NORS) [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]; Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/norsdashboard/
-
- CDC Reports of Selected Salmonella Outbreak Investigations. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/outbreaks.html.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

