Comparative Quantitation of Kokumi γ-Glutamyl Peptides in Spanish Dry-Cured Ham under Salt-Reduced Production
- PMID: 37509906
- PMCID: PMC10378828
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12142814
Comparative Quantitation of Kokumi γ-Glutamyl Peptides in Spanish Dry-Cured Ham under Salt-Reduced Production
Abstract
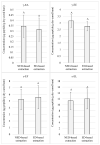
Salting is a crucial step during the production of dry-cured ham and it is not well known whether it has an impact on the generation of taste-active peptides. The present study focused on the quantitation of kokumi γ-glutamyl peptides in low-salted Spanish dry-cured hams with 12 months of processing. By using mass spectrometry, peptides were quantitated from samples obtained after ethanolic deproteinization-based and non-ethanolic deproteinization-based extraction methods. Peptides γ-EA, γ-EE, and γ-EL registered mean values of 0.31, 2.75, and 11.35 µg/g of dry-cured ham, respectively, with no differences observed between both extraction protocols. However, γ-EF, γ-EM, γ-EV, γ-EW, γ-EY, and γ-EVG presented significantly (p < 0.05) higher concentrations in the ethanolic deproteinized samples showing values of 5.58, 4.13, 13.90, 0.77, 3.71, and 0.11 µg/g of dry-cured ham, respectively. These outcomes reflect the importance of protocols for the extraction of peptides to achieve the most feasible results. In addition, potential precursors for the formation of γ-glutamyl peptides are generated during dry-curing under salt restriction. The kokumi activity of these γ-glutamyl peptides could enhance the sensory attributes countering the taste deficiencies caused by the salt restriction.
Keywords: dry-cured ham; kokumi; peptide extraction; peptidomics; salt; γ-glutamyl peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of kokumi γ-glutamyl short peptides in Spanish dry-cured ham during its processing.Meat Sci. 2023 Dec;206:109323. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2023.109323. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Meat Sci. 2023. PMID: 37708620
-
Identification and Quantitation of Bioactive and Taste-Related Dipeptides in Low-Salt Dry-Cured Ham.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 24;23(5):2507. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052507. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269650 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of oxidation on the cardioprotective properties of the bioactive dipeptide AW in dry-cured ham.Food Res Int. 2022 Dec;162(Pt B):112128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112128. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36461411
-
Perspectives in the Use of Peptidomics in Ham.Proteomics. 2018 Sep;18(18):e1700422. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201700422. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29882253 Review.
-
Current progress in kokumi-active peptides, evaluation and preparation methods: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(5):1230-1241. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1837726. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33103468 Review.
References
-
- Sentandreu M.A., Toldrá F. Dipeptidyl Peptidase Activities along the Processing of Serrano Dry-Cured Ham. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2001;213:83–87. doi: 10.1007/s002170100355. - DOI
-
- Armenteros M., Aristoy M.C., Barat J.M., Toldrá F. Biochemical Changes in Dry-Cured Loins Salted with Partial Replacements of NaCl by KCl. Food Chem. 2009;117:627–633. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.056. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

