Sestrin2 as a Potential Target in Hypertension
- PMID: 37510117
- PMCID: PMC10378131
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13142374
Sestrin2 as a Potential Target in Hypertension
Abstract
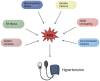
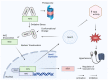
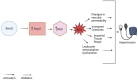
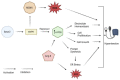
Hypertension is a highly complex, intricate condition affecting millions of individuals across the globe. Nearly half of adults in the United States are diagnosed with hypertension, with incident rates projected to rise over the next decade. Hypertension is a precursor to many cardiovascular diseases including atherosclerosis, stroke, myocardial infarction, heart failure, and peripheral artery disease. This review describes the major processes contributing to the development of hypertension and how Sestrin2 (Sesn2), an antioxidative protein, could be a potential target in the treatment of hypertension. In hypertension, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production is a critical component in the etiology of the condition. The increased ROS in hypertension is derived from a variety of sources, all of which are covered in depth in this review. Increased ROS is generated from mitochondrial stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, NADPH oxidase (NOX) overactivity, and the uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxidase synthase (eNOS). Sesn2, a highly conserved, stress-inducible protein, has the structural and functional characteristics to be a potential therapeutic target to alleviate the progression of hypertension. The structure, function, genetics, and characteristics of Sesn2 are presented in the review. The Nrf2/Sesn2, Sesn2/AMPK/mTOR, and Sesn2/Angiotensin II signaling pathways are described in detail in this review. Sesn2 can be utilized in a multitude of ways as a therapeutic modality in hypertension. This review explores potential Sesn2 inducers and activators and how Sesn2 can be incorporated into gene therapy for the treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: Sesn2; redox homeostasis; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dosh S.A. The diagnosis of essential and secondary hypertension in adults. J. Fam. Pract. 2001;50:707–712. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

