Machine-Learning-Based Diagnostics of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Using Multi-Chamber Wall Motion Analyses
- PMID: 37510168
- PMCID: PMC10377893
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13142426
Machine-Learning-Based Diagnostics of Cardiac Sarcoidosis Using Multi-Chamber Wall Motion Analyses
Abstract
Background: Hindered by its unspecific clinical and phenotypical presentation, cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) remains a challenging diagnosis.
Objective: Utilizing cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR), we acquired multi-chamber volumetrics and strain feature tracking for a support vector machine learning (SVM)-based diagnostic approach to CS.
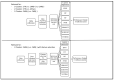
Method: Forty-five CMR-negative (CMR(-), 56.5(53.0;63.0)years), eighteen CMR-positive (CMR(+), 64.0(57.8;67.0)years) sarcoidosis patients and forty-four controls (CTRL, 56.5(53.0;63.0)years)) underwent CMR examination. Cardiac parameters were processed using the classifiers of logistic regression, KNN(K-nearest-neighbor), DT (decision tree), RF (random forest), SVM, GBoost, XGBoost, Voting and feature selection.
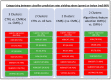
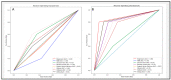
Results: In a three-cluster analysis of CTRL versus vs. CMR(+) vs. CMR(-), RF and Voting classifier yielded the highest prediction rates (81.82%). The two-cluster analysis of CTRL vs. all sarcoidosis (All Sarc.) yielded high prediction rates with the classifiers logistic regression, RF and SVM (96.97%), and low prediction rates for the analysis of CMR(+) vs. CMR(-), which were augmented using feature selection with logistic regression (89.47%).
Conclusion: Multi-chamber cardiac function and strain-based supervised machine learning provides a non-contrast approach to accurately differentiate between healthy individuals and sarcoidosis patients. Feature selection overcomes the algorithmically challenging discrimination between CMR(+) and CMR(-) patients, yielding high accuracy predictions. The study findings imply higher prevalence of cardiac involvement than previously anticipated, which may impact clinical disease management.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance; cardiac sarcoidosis 3; cardiac strain; machine learning 2; multi-chamber analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Soto-Gomez N., Peters J.I., Nambiar A.M. Diagnosis and Management of Sarcoidosis. Am. Fam. Physician. 2016;93:840–848. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

