Capturing the Kidney Transcriptome by Urinary Extracellular Vesicles-From Pre-Analytical Obstacles to Biomarker Research
- PMID: 37510317
- PMCID: PMC10379145
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14071415
Capturing the Kidney Transcriptome by Urinary Extracellular Vesicles-From Pre-Analytical Obstacles to Biomarker Research
Abstract
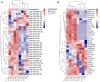
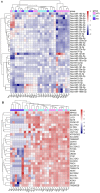
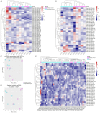
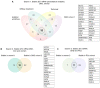
Urinary extracellular vesicles (uEV) hold non-invasive RNA biomarkers for genitourinary tract diseases. However, missing knowledge about reference genes and effects of preanalytical choices hinder biomarker studies. We aimed to assess how preanalytical variables (urine storage temperature, isolation workflow) affect diabetic kidney disease (DKD)-linked miRNAs or kidney-linked miRNAs and mRNAs (kidney-RNAs) in uEV isolates and to discover stable reference mRNAs across diverse uEV datasets. We studied nine raw and normalized sequencing datasets including healthy controls and individuals with prostate cancer or type 1 diabetes with or without albuminuria. We focused on kidney-RNAs reviewing literature for DKD-linked miRNAs from kidney tissue, cell culture and uEV/urine experiments. RNAs were analyzed by expression heatmaps, hierarchical clustering and selecting stable mRNAs with normalized counts (>200) and minimal coefficient of variation. Kidney-RNAs were decreased after urine storage at -20 °C vs. -80 °C. Isolation workflows captured kidney-RNAs with different efficiencies. Ultracentrifugation captured DKD -linked miRNAs that separated healthy and diabetic macroalbuminuria groups. Eleven mRNAs were stably expressed across the datasets. Hence, pre-analytical choices had variable effects on kidney-RNAs-analyzing kidney-RNAs complemented global correlation, which could fade differences in some relevant RNAs. Replicating prior DKD-marker results and discovery of candidate reference mRNAs encourages further uEV biomarker studies.
Keywords: diabetic kidney disease; exosomes; mRNA; miRNA; reference genes; sequencing; urinary extracellular vesicles; urine.
Conflict of interest statement
K.B., O.D.P, H.H., T.T. and M.P. declare no conflict of interest. P-H.G. has received research grants from Eli Lilly and Roche; is an advisory board member for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cebix, Eli Lilly, Jansen, MSD, Novartis, NovoNordisk and Sanofi; and has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Elo Water, Genzyme, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. K.B., O.D.P, H.H., T.T. and M.P. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of urinary extracellular vesicle isolation methods for transcriptomic biomarker research in diabetic kidney disease.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Dec;10(2):e12038. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12038. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33437407 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles: Assessment of pre-analytical variables and development of a quality control with focus on transcriptomic biomarker research.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Oct;10(12):e12158. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12158. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34651466 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma and urinary extracellular vesicle microRNAs and their related pathways in diabetic kidney disease.Genomics. 2022 Jul;114(4):110407. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110407. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35716820
-
Urinary Extracellular Vesicle: A Potential Source of Early Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarker in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Jun 5;131(11):1357-1364. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.232801. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29786051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Are a Novel Tool to Monitor Allograft Function in Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10499. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910499. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638835 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
miR-182, miR-221 and miR-222 are potential urinary extracellular vesicle biomarkers for canine urothelial carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69070-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095540 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles in childhood kidney diseases.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Aug;39(8):2293-2300. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-06243-y. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38093081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Detection, Precision Treatment, Recurrence Monitoring: Liquid Biopsy Transforms Colorectal Cancer Therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025;25(6):586-619. doi: 10.2174/0115680096295070240318075023. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 38623975 Review.
-
Urinary podocyte markers in diabetic kidney disease.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024 May;43(3):274-286. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.23.109. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38325865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodosthenous R.S., Hutchins E., Reiman R., Yeri A.S., Srinivasan S., Whitsett T.G., Ghiran I., Silverman M.G., Laurent L.C., Van Keuren-Jensen K., et al. Profiling Extracellular Long RNA Transcriptome in Human Plasma and Extracellular Vesicles for Biomarker Discovery. iScience. 2020;23:101182. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101182. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

