Impact of COVID-19 Diagnosis on Mortality in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Admitted during the 2020 Pandemic in Italy
- PMID: 37510675
- PMCID: PMC10380878
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12144560
Impact of COVID-19 Diagnosis on Mortality in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Admitted during the 2020 Pandemic in Italy
Abstract
Aims: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the event rate of patients with ischemic stroke has been poorly investigated. We sought to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 infection on mortality in patients with ischemic stroke admitted during the 2020 pandemic in Italy.
Methods: We analyzed a nationwide, comprehensive, and universal administrative database of patients who were admitted for ischemic stroke during and after the national lockdown for the COVID-19 infection in 2020, and the equivalent periods over the previous 5 years in Italy. The 2020 observed hospitalization and mortality rates of stroke patients with and without COVID-19 infection were compared with the expected rates, in accordance with the trend of the previous 5 years.
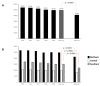
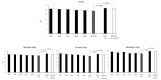
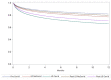
Results: During the period of observation, 300,890 hospitalizations for ischemic stroke occurred in Italy. In 2020, 41,302 stroke patients (1102 with concomitant COVID-19 infection) were admitted at 771 centers. The rate of admissions for ischemic stroke during the 2020 pandemic was markedly reduced compared with previous years (percentage change vs. 2015: -23.5). Based on the 5 year trend, the 2020 expected 30 day and 1 year mortality rates were 9.8% and 23.9%, respectively, and the observed incidence of death rates were 12.2% and 26.7%, respectively (both p < 0.001). After multiple corrections, higher rates of mortality were observed among patients admitted for stroke with a concomitant COVID-19 diagnosis.
Conclusions: During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 in Italy, the rate of hospitalizations for ischemic stroke was dramatically reduced, although both the 30 day and 1 year mortality rates increased compared with the previous 5 year trend.
Keywords: COVID-19; hospitalizations; mortality; national outbreak; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of COVID-19 Diagnosis on Mortality in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Hospitalized during the National Outbreak in Italy.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 10;11(24):7350. doi: 10.3390/jcm11247350. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36555967 Free PMC article.
-
Covid-19 diagnosis and mortality in patients with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction admitted in Italy during the national outbreak.Int J Cardiol. 2023 Jan 1;370:447-453. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.11.008. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Int J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36356695 Free PMC article.
-
Hospitalizations for Stroke in France During the COVID-19 Pandemic Before, During, and After the National Lockdown.Stroke. 2021 Apr;52(4):1362-1369. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032312. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33626900
-
The impact of COVID-19 on acute ischemic stroke admissions: Analysis from a community-based tertiary care center.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Dec;29(12):105344. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105344. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 33049464 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and a national lockdown on hospitalizations for stroke and related 30-day mortality in France: A nationwide observational study.Eur J Neurol. 2021 Oct;28(10):3279-3288. doi: 10.1111/ene.14831. Epub 2021 Mar 29. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33738913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aveyard P., Gao M., Lindson N., Hartmann-Boyce J., Watkinson P., Young D., Coupland C.A.C., Tan P.S., Clift A.K., Harrison D., et al. Association between pre-existing respiratory disease and its treatment, and severe COVID-19: A population cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021;9:909–923. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

