Bruxism and Botulinum Injection: Challenges and Insights
- PMID: 37510701
- PMCID: PMC10380379
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12144586
Bruxism and Botulinum Injection: Challenges and Insights
Abstract
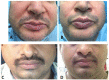
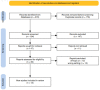
Botulinum toxin (BTA) is a bacterial-derived extract that can inhibit muscle contraction, acting directly on the absorption of acetylcholine. Thanks to this property, botulinum has been used in aesthetic and general medicine for several years. Nowadays, the use of botulinum toxin is being deepened to address the problem of bruxism. In this scoping review, the results of the studies in the literature of the last 10 years were analyzed. Indeed, 12 reports (found on PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus, entering the keywords "BRUXISM" and "BOTULINUM TOXIN") were deemed eligible for inclusion in this review. In the studies reviewed, BTA was injected into different muscle groups: masseters, masseter and temporalis or masseter, temporalis, and medial pterygoid. Botulinum toxin injection is a viable therapeutic solution, especially in patients with poor compliance or without improvement in conventional treatment.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; bruxism; dentistry; injection; masseters; medial pterygoids; review; temporalis; type A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Klasser G.D., Rei N., Lavigne G.J. Sleep Bruxism Etiology: The Evolution of a Changing Paradigm. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2015;81:f2. - PubMed
-
- Quinzi V., Saccomanno S., Manenti R.J., Giancaspro S., Coceani Paskay L., Marzo G. Efficacy of Rapid Maxillary Expansion with or without Previous Adenotonsillectomy for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Based on Polysomnographic Data: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:6485. doi: 10.3390/app10186485. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

