An Easy-To-Use External Fixator for All Hostile Environments, from Space to War Medicine: Is It Meant for Everyone's Hands?
- PMID: 37510879
- PMCID: PMC10381442
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12144764
An Easy-To-Use External Fixator for All Hostile Environments, from Space to War Medicine: Is It Meant for Everyone's Hands?
Abstract
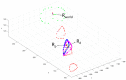
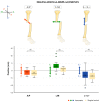
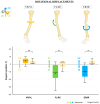
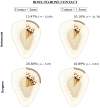
Long bone fractures in hostile environments pose unique challenges due to limited resources, restricted access to healthcare facilities, and absence of surgical expertise. While external fixation has shown promise, the availability of trained surgeons is limited, and the procedure may frighten unexperienced personnel. Therefore, an easy-to-use external fixator (EZExFix) that can be performed by nonsurgeon individuals could provide timely and life-saving treatment in hostile environments; however, its efficacy and accuracy remain to be demonstrated. This study tested the learning curve and surgical performance of nonsurgeon analog astronauts (n = 6) in managing tibial shaft fractures by the EZExFix during a simulated Mars inhabited mission, at the Mars Desert Research Station (Hanksville, UT, USA). The reduction was achievable in the different 3D axis, although rotational reductions were more challenging. Astronauts reached similar bone-to-bone contact compared to the surgical control, indicating potential for successful fracture healing. The learning curve was not significant within the limited timeframe of the study (N = 4 surgeries lasting <1 h), but the performance was similar to surgical control. The results of this study could have important implications for fracture treatment in challenging or hostile conditions on Earth, such as war or natural disaster zones, developing countries, or settings with limited resources.
Keywords: developing countries; external fixator; hostile environments; learning curve; space; tibial shaft fracture; war medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Manon J., Saint-Guillain M., Pletser V., Buckland D.M., Vico L., Dobney W., Baatout S., Wain C., Jacobs J., Comein A. Adequacy of In-Mission Training to Treat Tibial Shaft Fractures in Mars Analog Testing. 2023. [(accessed on 25 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2967843/v1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertol M.J., Van den Bergh R., Trelles Centurion M., Kenslor Ralph D.H., Basimuoneye Kahutsi J.-P., Qayeum Qasemy A., Jean J., Majuste A., Kubuya Hangi T., Safi S., et al. Saving Life and Limb: Limb Salvage Using External Fixation, a Multi-Centre Review of Orthopaedic Surgical Activities in Médecins Sans Frontières. Int. Orthop. 2014;38:1555–1561. doi: 10.1007/s00264-014-2451-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

