Suppression of Indoxyl Sulfate Accumulation Reduces Renal Fibrosis in Sulfotransferase 1a1-Deficient Mice
- PMID: 37511089
- PMCID: PMC10380001
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411329
Suppression of Indoxyl Sulfate Accumulation Reduces Renal Fibrosis in Sulfotransferase 1a1-Deficient Mice
Abstract
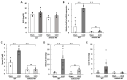
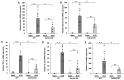
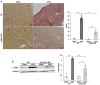
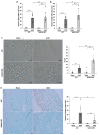
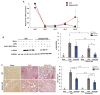
Renal fibrosis is the final manifestation of chronic kidney disease (CKD); its prevention is vital for controlling CKD progression. Indoxyl sulfate (IS), a typical sulfate-conjugated uremic solute, is produced in the liver via the enzyme sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A1 and accumulates significantly during CKD. We investigated the toxicopathological role of IS in renal fibrosis using Sult1a1-KO mice and the underlying mechanisms. The unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) model was created; kidney IS concentrations, inflammation, and renal fibrosis were assessed on day 14. After UUO treatment, inflammation and renal fibrosis were exacerbated in WT mice, with an accumulation of IS in the kidney. However, they were significantly suppressed in Sult1a1-KO mice. CD206+ expression was upregulated, and β-catenin expression was downregulated in Sult1a1-KO mice. To confirm the impact of erythropoietin (EPO) on renal fibrosis, we evaluated the time-dependent expression of EPO. In Sult1a1-KO mice, EPO mRNA expression was improved considerably; UUO-induced renal fibrosis was further attenuated by recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO). Thus, UUO-induced renal fibrosis was alleviated in Sult1a1-KO mice with a decreased accumulation of IS. Our findings confirmed the pathological role of IS in renal fibrosis and identified SULT1A1 as a new therapeutic target enzyme for preventing and attenuating renal fibrosis.
Keywords: indoxyl sulfate; renal fibrosis; sulfotransferase 1a1-deficient mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sharma S.K., Zou H., Togtokh A., Ene-Iordache B., Carminati S., Remuzzi A., Wiebe N., Ayyalasomayajula B., Perico N., Remuzzi G., et al. Burden of CKD, proteinuria, and cardiovascular risk among Chinese, Mongolian, and Nepalese participants in the International Society of Nephrology screening programs. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010;56:915–927. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.06.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T., Ise M., Hirata M., Endo K., Ito Y., Seo H., Niwa T. Indoxyl sulfate stimulates renal synthesis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and progression of renal failure. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1997;63:S211–S214. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

