Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Trap: The Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Tuberculosis
- PMID: 37511144
- PMCID: PMC10379580
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411385
Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Trap: The Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Tuberculosis
Abstract
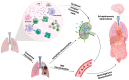
Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex causes tuberculosis (TB), a disease that causes pulmonary inflammation but can also affect other tissues. Despite macrophages having a defined role in TB immunopathogenesis, other innate immune cells, such as neutrophils, are involved in this process. These cells have high phagocytic ability and a microbial-killing machine comprised of enzymes, antimicrobial peptides, and reactive oxygen species. In the last two decades, a new neutrophil immune response, the neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), has been intensely researched. NETs comprise DNA associated with histones, enzymes, and antimicrobial peptides. These structures are related to antimicrobial immune response and some immuno-pathogenesis mechanisms. This mini review highlights the role of NETs in tuberculosis and how they can be helpful as a diagnostic tool and/or therapeutic target.
Keywords: NETs; innate immunity; mycobacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nogueira B.M.F., Krishnan S., Barreto-Duarte B., Araújo-Pereira M., Queiroz A.T.L., Ellner J.J., Salgame P., Scriba T.J., Sterling T.R., Gupta A., et al. Diagnostic biomarkers for active tuberculosis: Progress and challenges. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022;14:e14088. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

