Effects of Angiotensin 1-7 and Mas Receptor Agonist on Renal System in a Rat Model of Heart Failure
- PMID: 37511227
- PMCID: PMC10380355
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411470
Effects of Angiotensin 1-7 and Mas Receptor Agonist on Renal System in a Rat Model of Heart Failure
Abstract
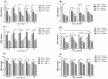
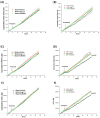
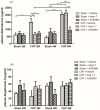
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is often associated with impaired kidney function. Over- activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) contributes to avid salt/water retention and cardiac hypertrophy in CHF. While the deleterious effects of angiotensin II (Ang II) in CHF are well established, the biological actions of angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) are not fully characterized. In this study, we assessed the acute effects of Ang 1-7 (0.3, 3, 30 and 300 ng/kg/min, IV) on urinary flow (UF), urinary Na+ excretion (UNaV), glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow )RPF) in rats with CHF induced by the placement of aortocaval fistula. Additionally, the chronic effects of Ang 1-7 (24 µg/kg/h, via intra-peritoneally implanted osmotic minipumps) on kidney function, cardiac hypertrophy and neurohormonal status were studied. Acute infusion of either Ang 1-7 or its agonist, AVE 0991, into sham controls, but not CHF rats, increased UF, UNaV, GFR, RPF and urinary cGMP. In the chronic protocols, untreated CHF rats displayed lower cumulative UF and UNaV than their sham controls. Chronic administration of Ang 1-7 and AVE 0991 exerted significant diuretic, natriuretic and kaliuretic effects in CHF rats, but not in sham controls. Serum creatinine and aldosterone levels were significantly higher in vehicle-treated CHF rats as compared with controls. Treatment with Ang 1-7 and AVE 0991 reduced these parameters to comparable levels observed in sham controls. Notably, chronic administration of Ang 1-7 to CHF rats reduced cardiac hypertrophy. In conclusion, Ang 1-7 exerts beneficial renal and cardiac effects in rats with CHF. Thus, we postulate that ACE2/Ang 1-7 axis represents a compensatory response to over-activity of ACE/AngII/AT1R system characterizing CHF and suggest that Ang 1-7 may be a potential therapeutic agent in this disease state.
Keywords: ACE2; MasR; angiotensin 1-7; heart failure; kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pulmonary, cardiac and renal distribution of ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 in rats with heart failure: Potential implication for COVID-19 disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Apr;25(8):3840-3855. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16310. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33660945 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise training on circulating and skeletal muscle renin-angiotensin system in chronic heart failure rats.PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e98012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098012. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24859374 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-(1-7) in Paraventricular Nucleus Contributes to the Enhanced Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex and Sympathetic Activity in Chronic Heart Failure Rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(6):2523-2539. doi: 10.1159/000480214. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28848201 Free PMC article.
-
ACE2 of the heart: From angiotensin I to angiotensin (1-7).Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Feb 1;73(3):463-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.09.006. Epub 2006 Sep 19. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17049503 Review.
-
ACE2 and vasoactive peptides: novel players in cardiovascular/renal remodeling and hypertension.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):217-37. doi: 10.1177/1753944715597623. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26275770 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Renin-Angiotensin System in Diabetic Nephropathy: An Update.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(8):591-600. doi: 10.2174/0113895575344980250130062547. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39936412 Review.
-
Neurohumoral Activation in Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15472. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015472. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 on the dysfunction of renal Mas receptor in hypertension.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 5;20(8):e0329547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329547. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40763158 Free PMC article.
-
The RAAS Goodfellas in Cardiovascular System.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 31;12(21):6873. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216873. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

