Cyanocobalamin-Modified Colistin-Hyaluronan Conjugates: Synthesis and Bioactivity
- PMID: 37511308
- PMCID: PMC10380726
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411550
Cyanocobalamin-Modified Colistin-Hyaluronan Conjugates: Synthesis and Bioactivity
Abstract
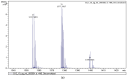
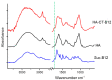
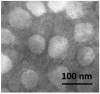
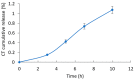
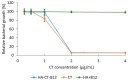
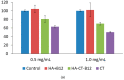
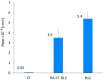
Polymeric drug delivery systems enhance the biopharmaceutical properties of antibiotics by increasing their bioavailability, providing programmable and controlled-release properties, and reducing toxicity. In addition, drug delivery systems are a promising strategy to improve the intestinal permeability of various antimicrobial agents, including colistin (CT). This study describes the modification of conjugates based on CT and hyaluronic acid (HA) with cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12). Vitamin B12 was chosen as a targeting ligand because it has its own absorption pathway in the small intestine. The resulting polysaccharide conjugates contained 95 μg/mg vitamin B12 and the CT content was 335 μg/mg; they consisted of particles of two sizes, 98 and 702 nm, with a ζ-potential of approximately -25 mV. An in vitro release test at pH 7.4 and pH 5.2 showed an ultra-slow release of colistin of approximately 1% after 10 h. The modified B12 conjugates retained their antimicrobial activity at the level of pure CT (minimum inhibitory concentration was 2 μg/mL). The resulting delivery systems also reduced the nephrotoxicity of CT by 30-40% (HEK 293 cell line). In addition, the modification of B12 improved the intestinal permeability of CT, and the apparent permeability coefficient of HA-CT-B12 conjugates was 3.5 × 10-6 cm/s, corresponding to an in vivo intestinal absorption of 50-100%. Thus, vitamin-B12-modified conjugates based on CT and HA may be promising oral delivery systems with improved biopharmaceutical properties.
Keywords: colistin; cyanocobalamin; hyaluronic acid; intestinal permeability; oral drug delivery; polymeric conjugates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Sharma A., Mittal K., Arora D., Ganti S.S. A comprehensive review on strategies for new drug discovery and enhanced productivity in research and development: Recent advancements and future prospectives. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2021;18:361–382. doi: 10.2174/1570193X17999200529100808. - DOI
-
- Who Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. [(accessed on 12 June 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-ba....
-
- Dubashynskaya N.V., Raik S.V., Dubrovskii Y.A., Demyanova E.V., Shcherbakova E.S., Poshina D.N., Shasherina A.Y., Anufrikov Y.A., Skorik Y.A. Hyaluronan/diethylaminoethyl chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes as carriers for improved colistin delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:8381. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

