Neurofilament-Light, a Promising Biomarker: Analytical, Metrological and Clinical Challenges
- PMID: 37511382
- PMCID: PMC10380627
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411624
Neurofilament-Light, a Promising Biomarker: Analytical, Metrological and Clinical Challenges
Abstract
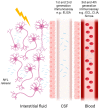
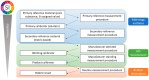
Neurofilament-light chain (Nf-L) is a non-specific early-stage biomarker widely studied in the context of neurodegenerative diseases (NDD) and traumatic brain injuries (TBI), which can be measured in biofluids after axonal damage. Originally measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), Nf-L can now be quantified in blood with the emergence of ultrasensitive assays. However, to ensure successful clinical implementation, reliable clinical thresholds and reference measurement procedures (RMP) should be developed. This includes establishing and distributing certified reference materials (CRM). As a result of the complexity of Nf-L and the number of circulating forms, a clear definition of what is measured when immunoassays are used is also critical to achieving standardization to ensure the long-term success of those assays. The use of powerful tools such as mass spectrometry for developing RMP and defining the measurand is ongoing. Here, we summarize the current methods in use for quantification of Nf-L in biofluid showing potential for clinical implementation. The progress and challenges in developing RMP and defining the measurand for Nf-L standardization of diagnostic tests are addressed. Finally, we discuss the impact of pathophysiological factors on Nf-L levels and the establishment of a clinical cut-off.
Keywords: biomarker; implementation; neurodegenerative disease; neurofilament-light; standardization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

