Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema
- PMID: 37511409
- PMCID: PMC10380452
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411649
Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema
Abstract
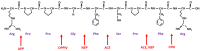
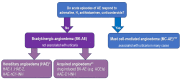
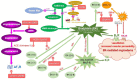
Bradykinin (BK) metabolism and its receptors play a central role in drug-induced angioedema (AE) without urticaria through increased vascular permeability. Many cardiovascular and diabetic drugs may cause BK-mediated AE. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and neprilysin inhibitors impair BK catabolism. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors reduce the breakdown of BK and substance P (SP). Moreover, angiotensin receptor blockers, thrombolytic agents, and statins may also induce BK-mediated AE. Understanding pathophysiological mechanisms is crucial for preventing and treating drug-induced AE.
Keywords: bradykinin metabolism; drug-induced angioedema.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

