Let-7a Downregulation Accompanied by KRAS Mutation Is Predictive of Lung Cancer Onset in Cigarette Smoke-Exposed Mice
- PMID: 37511536
- PMCID: PMC10380304
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411778
Let-7a Downregulation Accompanied by KRAS Mutation Is Predictive of Lung Cancer Onset in Cigarette Smoke-Exposed Mice
Abstract
Background: Let-7 is a tumor suppressor microRNA targeting the KRAS lung oncogene. Let-7a downregulation is reversible during the early stages of lung carcinogenesis but is irreversible in cancer cells. The aim of this study is to shed light on the relationship between oncogene (KRAS) mutation and let-7a downregulation in cigarette smoke (CS)-induced lung carcinogenesis.
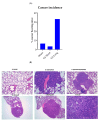
Methods: A total of 184 strain H Swiss albino mice were either unexposed (control) or exposed to CS for 2 weeks (short CS) or 8 months (long CS). After 8 months, the lungs were individually collected. The following end points have been evaluated: (a) DNA methylation of the let-7a gene promoter by bisulphite-PCR and pyrosequencing; (b) let-7a expression by qPCR; (c) KRAS mutation by DNA pyrosequencing; (d) cancer incidence by histopathological examination.
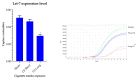
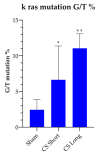
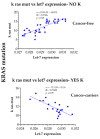
Results: let-7a expression decreased by 8.3% in the mice exposed to CS for two weeks (CS short) and by 33.4% (p ≤ 0.01) in the mice exposed to CS for 8 months (CS long). No significant difference was detected in the rate of let-7a-promoter methylation between the Sham-exposed mice (55.1%) and the CS short-(53%) or CS long (51%)-exposed mice. The percentage of G/T transversions in KRAS codons 12 and 13 increased from 2.3% (Sham) to 6.4% in CS short- and to 11.5% in CS long-exposed mice. Cancer incidence increased significantly in the CS long-exposed mice (11%) as compared to both the Sham (4%) and the CS short-exposed (2%) mice. In the CS long-exposed mice, the correlation between let-7a expression and the number of KRAS mutations was positive (R = +0.5506) in the cancer-free mice and negative (R = -0.5568) in the cancer-bearing mice.
Conclusions: The effects of CS-induced mutations in KRAS are neutralized by the high expression of let-7a in cancer-free mice (positive correlation) but not in cancer-bearing mice where an irreversible let-7a downregulation occurs (negative correlation). This result provides evidence that both genetic (high load of KRAS mutation) and epigenetic alterations (let-7a irreversible downregulation) are required to produce lung cancer in CS-exposed organisms.
Keywords: KRAS mutation; cigarette smoke; let-7a expression; lung cancer; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Let-7a regulates mammosphere formation capacity through Ras/NF-κB and Ras/MAPK/ERK pathway in breast cancer stem cells.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(11):1686-97. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1030547. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25955298 Free PMC article.
-
TP53 and let-7a micro-RNA regulate K-Ras activity in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 1;8(8):e70604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070604. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936455 Free PMC article.
-
High let-7a microRNA levels in KRAS-mutated colorectal carcinomas may rescue anti-EGFR therapy effects in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic disease.Oncologist. 2012;17(6):823-9. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0081. Epub 2012 May 14. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22584434 Free PMC article.
-
The RAS oncogene in brain tumors and the involvement of let-7 microRNA.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Apr 18;51(1):531. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09439-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38637419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular damage and lung tumors in cigarette smoke-exposed mice.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Mar;1340:75-83. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12697. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 25712567 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances on high-efficiency of microRNAs in different types of lung cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 20;23(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03133-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37986065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifestyle-Driven Variations in Nutrimiromic MicroRNA Expression Patterns across and beyond Genders.Life (Basel). 2024 Mar 15;14(3):390. doi: 10.3390/life14030390. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541714 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in lung cancer: insights into their functions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 27;12:1397788. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1397788. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38859962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends in microRNA profiling as a biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma via liquid biopsy: A bibliometric analysis.Narra J. 2025 Apr;5(1):e1372. doi: 10.52225/narra.v5i1.1372. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Narra J. 2025. PMID: 40352245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M., Zhaor A., Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Division of Cancer Prevention and Control. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2022.
-
- Lissowska J., Foretova L., Dabek J., Zaridze D., Szeszenia-Dabrowska N., Rudnai P., Fabianova E., Cassidy A., Mates D., Bencko V., et al. Family History and Lung Cancer Risk: Inter-national Muticentre Case-Control Study in Eastern and Central Europe and Meta-Analyses. Cancer Causes Control. 2010;21:1091–1104. doi: 10.1007/s10552-010-9537-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

