Recent Progress in the Characterization, Synthesis, Delivery Procedures, Treatment Strategies, and Precision of Antimicrobial Peptides
- PMID: 37511621
- PMCID: PMC10380191
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411864
Recent Progress in the Characterization, Synthesis, Delivery Procedures, Treatment Strategies, and Precision of Antimicrobial Peptides
Abstract
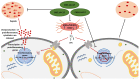
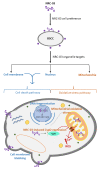
Infectious diseases are constantly evolving to bypass antibiotics or create resistance against them. There is a piercing alarm for the need to improve the design of new effective antimicrobial agents such as antimicrobial peptides which are less prone to resistance and possess high sensitivity. This would guard public health in combating and overcoming stubborn pathogens and mitigate incurable diseases; however, the emergence of antimicrobial peptides' shortcomings ranging from untimely degradation by enzymes to difficulty in the design against specific targets is a major bottleneck in achieving these objectives. This review is aimed at highlighting the recent progress in antimicrobial peptide development in the area of nanotechnology-based delivery, selectivity indices, synthesis and characterization, their doping and coating, and the shortfall of these approaches. This review will raise awareness of antimicrobial peptides as prospective therapeutic agents in the medical and pharmaceutical industries, such as the sensitive treatment of diseases and their utilization. The knowledge from this development would guide the future design of these novel peptides and allow the development of highly specific, sensitive, and accurate antimicrobial peptides to initiate treatment regimens in patients to enable them to have accommodating lifestyles.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; broad-spectrum; characterization; coating; doping; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shen X., Zhang Y., Mao Q., Huang Z., Yan T., Lin T., Chen W., Wang Y., Cai X., Liang Y. Peptide–Polymer Conjugates: A Promising Therapeutic Solution for Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2022;2022:7610951. doi: 10.1155/2022/7610951. - DOI
-
- Qin S., Xiao W., Zhou C., Pu Q., Deng X., Lan L., Liang H., Song X., Wu M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022;7:199. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

