Precision Medicine for More Oxygen (P4O2)-Study Design and First Results of the Long COVID-19 Extension
- PMID: 37511673
- PMCID: PMC10381397
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13071060
Precision Medicine for More Oxygen (P4O2)-Study Design and First Results of the Long COVID-19 Extension
Abstract
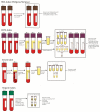
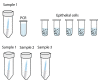
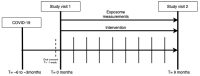
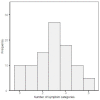
Introduction: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to the death of almost 7 million people, however, with a cumulative incidence of 0.76 billion, most people survive COVID-19. Several studies indicate that the acute phase of COVID-19 may be followed by persistent symptoms including fatigue, dyspnea, headache, musculoskeletal symptoms, and pulmonary functional-and radiological abnormalities. However, the impact of COVID-19 on long-term health outcomes remains to be elucidated. Aims: The Precision Medicine for more Oxygen (P4O2) consortium COVID-19 extension aims to identify long COVID patients that are at risk for developing chronic lung disease and furthermore, to identify treatable traits and innovative personalized therapeutic strategies for prevention and treatment. This study aims to describe the study design and first results of the P4O2 COVID-19 cohort. Methods: The P4O2 COVID-19 study is a prospective multicenter cohort study that includes nested personalized counseling intervention trial. Patients, aged 40-65 years, were recruited from outpatient post-COVID clinics from five hospitals in The Netherlands. During study visits at 3-6 and 12-18 months post-COVID-19, data from medical records, pulmonary function tests, chest computed tomography scans and biological samples were collected and questionnaires were administered. Furthermore, exposome data was collected at the patient's home and state-of-the-art imaging techniques as well as multi-omics analyses will be performed on collected data. Results: 95 long COVID patients were enrolled between May 2021 and September 2022. The current study showed persistence of clinical symptoms and signs of pulmonary function test/radiological abnormalities in post-COVID patients at 3-6 months post-COVID. The most commonly reported symptoms included respiratory symptoms (78.9%), neurological symptoms (68.4%) and fatigue (67.4%). Female sex and infection with the Delta, compared with the Beta, SARS-CoV-2 variant were significantly associated with more persisting symptom categories. Conclusions: The P4O2 COVID-19 study contributes to our understanding of the long-term health impacts of COVID-19. Furthermore, P4O2 COVID-19 can lead to the identification of different phenotypes of long COVID patients, for example those that are at risk for developing chronic lung disease. Understanding the mechanisms behind the different phenotypes and identifying these patients at an early stage can help to develop and optimize prevention and treatment strategies.
Keywords: infectious disease; long COVID; precision medicine; prospective observational cohort study.
Conflict of interest statement
M.I. Abdel-Aziz has nothing to declare. N. Baalbaki has nothing to declare. S. Bazdar has nothing to declare. I. Beekers has nothing to declare. R.J.H.C.G. Beijers has nothing to declare. J.M. Blankestijn has nothing to declare. M. van de Berge has nothing to declare. J.J.P. van den Bergh has a research funding from UCB and Amgen (outside P4O2). L.D. Bloemsma has nothing to declare. H.J. Bogaard received a Grant support Ferrer (Janssen, MSD). C.D.C. Born has nothing to declare. M.S.G.M. Bracke is the Co-founder of Clear. M.E.B. Cornelissen has nothing to declare. J.W.F. Dagelet received personal fees from the start-up company Breathomix BV. A.M. van der Does has nothing to declare. G.S. Downward has nothing to declare. C.M. van Drunen has nothing to declare. J.W. Duitman will receive financial support from Boehringer and Abbvie for the P4O2 ILD cohort. D. Gach has nothing to declare. J. Garssen has nothing to declare. J.J.M. Geelhoed has nothing to declare. J. Glastra is employee at Quantib. K. Golebski has nothing to declare. I.H. Heijink has a Research grant from Boeheringer Ingelheim outside the scope of the submitted work. P.S. Hiemstra has nothing to declare. J.C.S. Holtjer has nothing to declare. S. Holverda has nothing to declare. L. Houweling has nothing to declare. J.J.L. Jacobs has nothing to declare. R. Jonker has nothing to declare. P.J.M. Kuks has nothing to declare. A.K.A.L. Kwee has nothing to declare. R.C.J. Langen has nothing to declare. A.H. Maitland-van der Zee has received research grants outside the submitted work from GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie and Vertex, she is the PI of P4O2 (Precision Medicine for more Oxygen), a public private partnership co-funded by Health~Holland involving many private partners that contribute in-cash and/or in-kind (Aparito, Boehringer Ingelheim, Breathomix, Clear, Danone Nutricia Research, Fluidda, MonitAir, Ncardia, Ortec Logiqcare, Philips, Quantib-U, RespiQ, Roche, Smartfish, SODAQ, Thirona, TopMD and Novartis), and she has served in advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK, and Boehringer Ingelheim with money paid to her institution. M.M.A. Van Melle is advisor and previous researcher in conquest and prevail research project, funded by Optimum Patient Care and AstraZeneca.P. Moeskops is employee at Quantib. F.A.A. Mohamed Hoesein has nothing to declare. J. Mosayebi Amroabadi has nothing to declare. L. Noij has nothing to declare. E.J. Nossent has speaker fees for lectures and educational events (Janssen, Bayer/MSD, Astra Zeneca) United Therapeutics/Ferrer, Boehringer Ingelheim B.V., Chiesi. J. Olsson is employed at Smartfish which produce Remune (which is used in P4O2 as oral nutrition product). J. Otker has nothing to declare. S.D. Pouwels has an affiliation. B.R. Rae has nothing to declare. L.B. Richards has nothing to declare. A. Rodriguez Ruiz has nothing to declare. D.W. Schaminee has nothing to declare. A.M.W.J. Schols has nothing to declare. L.T. Schuurman has nothing to declare. S. Shahbazi Khamas has nothing to declare. G. Slingers receives personal fees from the company Breathomix BV. M. Tamarit receives personal fees from the company Breathomix BV. G.F. Vasse has nothing to declare. I. Verkouter has nothing to declare. R. de Vries receives personal fees and has a substantial interest in the company Breathomix BV. Y. de Wit-van Wijck has nothing to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Dixon B.E., Wools-Kaloustian K., Fadel W.F., Duszynski T.J., Yiannoutsos C., Halverson P.K., Menachemi N. Symptoms and symptom clusters associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in community-based populations: Results from a statewide epidemiological study. Public Glob. Health. 2020;16:e0241875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241875. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

