Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Measurement: A Multimarker Approach to Diagnosis and Prognosis in Acute Heart Failure
- PMID: 37511766
- PMCID: PMC10381388
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13071155
Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Measurement: A Multimarker Approach to Diagnosis and Prognosis in Acute Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Acute heart failure (AHF) is a major cause of hospitalization and mortality worldwide. Early and accurate diagnosis, as well as effective risk stratification, are essential for optimizing clinical management and improving patient outcomes. In this context, biomarkers have gained increasing interest in recent years as they can provide important diagnostic and prognostic information in patients with AHF.
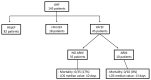
Aim and methods: The primary objective of the present study was to compare the levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM), and C-reactive protein (CRP) between patients diagnosed with acute heart failure (AHF) and those without AHF and sepsis. Furthermore, the study aimed to assess the diagnostic and prognostic value of the use of a multimarker approach in AHF patients. To achieve these objectives, a total of 145 patients with AHF and 127 patients without AHF and sepsis, serving as the control group, were consecutively enrolled in the study.
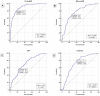
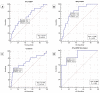
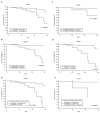
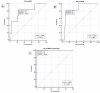
Results: Levels of MR-proADM (median: 2.07; (25th-75th percentiles: 1.40-3.02) vs. 1.11 (0.83-1.71) nmol/L, p < 0.0001), and NT-proBNP (5319 (1691-11,874) vs. 271 (89-931.5) pg/mL, p < 0.0001) were significantly higher in patients with AHF compared to controls, whereas CRP levels did not show significant differences. The mortality rate in the AHF group during in-hospital stay was 12%, and the rate of new re-admission for AHF within 30 days after discharge was 10%. During in-hospital follow-up, Cox regression analyses showed that levels of NT-proBNP > 10,132 pg/mL (hazard ratio (HR) 2.97; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.13-7.82; p = 0.0284) and levels of MR-proADM > 2.8 nmol/L (HR: 8.57; CI: 2.42-30.28; p = 0.0009) predicted mortality. The combined use of MR-proADM and NT-proBNP provided significant additive predictive value for mortality and new re-admission for AHF at 30 days after discharge. A logistic regression analysis showed that the presence of NT-proBNP pg/mL > 12,973 pg mL and/or MR-proADM > 4.2 nmol/L predicted hospital re-admission within 30 days (OR: 3.23; CI: 1.05-9.91; p = 0.041).
Conclusion: The combined assay of MR-proADM and NT-proBNP could be helpful in accurately identifying AHF and in defining prognosis and re-admission for AHF. The complementary use of these biomarkers can provide a useful clinical evaluation of AHF while also orienting clinicians to the pathophysiology underlying heart damage and assisting them in tailoring therapy.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP); acute heart failure (AHF); creatinine; mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., Chioncel O., et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) with the Special Contributio. Eur. Heart J. 2021;42:3599–3726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P., Voors A.A., Anker S.D., Bueno H., Cleland J.G.F., Coats A.J.S., Falk V., González-Juanatey J.R., Harjola V.-P., Jankowska E.A., et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the Special Contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:2129–2200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128. - DOI - PubMed
-
- James S.L., Abate D., Abate K.H., Abay S.M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Abdelalim A., et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 354 Diseases and Injuries for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

