The Effects of Crystalline Admixture on the Self-Healing Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mortar with Internally Added Superabsorbent Polymer
- PMID: 37512327
- PMCID: PMC10386621
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16145052
The Effects of Crystalline Admixture on the Self-Healing Performance and Mechanical Properties of Mortar with Internally Added Superabsorbent Polymer
Abstract
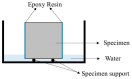
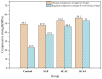
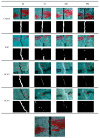
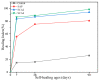
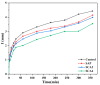
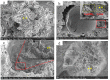
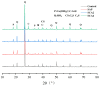
Crystalline admixture (CA) can be incorporated into concrete to achieve self-healing of concrete cracks. In this study, both CA and superabsorbent polymer (SAP) were used as self-healing agents to investigate the effects of CA on the self-healing performance and mechanical properties of mortar with internally added SAP at different self-healing ages. The healing effect of cracks in mortar is assessed by crack observation and impermeability. The structure and composition of the filler in the cracks were analyzed by microscopic experiment. The experimental results indicate that CA enhances the healing of cracks in mortar specimens. The chemical reactions of CA primarily contribute to significantly improving the early-age crack-healing ability of the specimens, and the water absorption and expansion ability as well as the internal curing effect of SAP also facilitate the crack-healing process. Increasing the CA content leads to an increase in the Ca/Si ratio of C-S-H, causing a transition from a layered structure to a more compact needle-like structure. When 4% CA was added to the mortar, it resulted in an adequate formation of needle-like C-S-H structures, which eventually penetrate and fill the pits formed by SAP, compensating for the strength loss caused by SAP.
Keywords: crack; crystalline admixture; mortar; self-healing; superabsorbent polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mehta P.K., Monteiro P.J.M. Concrete, Microstructure, Properties, and Materials. McGraw-Hill Education; New York, NY, USA: 2014.
-
- He X., Amin M.N., Khan K., Ahmad W., Althoey F., Vatin N.I. Self-healing concrete: A scientometric analysis-based review of the research development and scientific mapping. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022;17:e01521. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01521. - DOI
-
- Yu S., Jin H. Modeling of the corrosion-induced crack in concrete contained transverse crack subject to chloride ion penetration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020;258:119645. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119645. - DOI
-
- Abbas Y., Pargar F., Koleva D.A., van Breugel K., Olthuis W., van den Berg A. Non-destructive measurement of chloride ions concentration in concrete—A comparative analysis of limitations and prospects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018;174:376–387. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.135. - DOI
-
- Ganjian E., Pouya H.S. Effect of magnesium and sulfate ions on durability of silica fume blended mixes exposed to the seawater tidal zone. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005;35:1332–1343. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.09.028. - DOI
Grants and funding
- No.2572022DX10/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities Science
- No.GZ20220062/Heilongjiang Province Key Research and Development Plan Project "Nano-modified EVA and SBR compounding technology and its application in pavement crack prevention and control in cold regions."
- Analysis and Testing Center of Northeast Forestry University/Northeast Forestry University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

