Synthesis and Characterization of Ciprofloxacin Loaded Star-Shaped Polycaprolactone-Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels for Oral Delivery
- PMID: 37512693
- PMCID: PMC10383659
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14071382
Synthesis and Characterization of Ciprofloxacin Loaded Star-Shaped Polycaprolactone-Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogels for Oral Delivery
Abstract
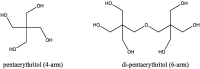
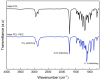
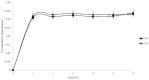
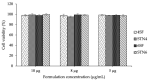
The administration of poorly water-soluble drugs represents a relevant problem due to the low body fluids transport efficiency through hydrophilic hydrogels. Star-shaped co-polymers, i.e., amphiphilic polymers such as those with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic outer shell, can be used to improve weak interactions with drugs, with relevant benefits in terms of administration and controlled delivery. In this work, two different co-polymers, four-arm star-shaped PCL-PEG and six-arm star-shaped PCL-PEG, were synthesized via ring-opening polymerization to be loaded with ciprofloxacin. 1H-NMR and FTIR analyses confirmed that PCL arms were successfully grafted to the mPEG backbone, while DSC analysis indicated similar crystallinity and melting point, ranging from 56 to 60 °C, independent of the different co-polymer architecture. Therefore, both star-shaped PCL-PEGs were investigated as cargo device for ciprofloxacin. No significant differences were observed in terms of drug entrapment efficiency (>95%) and drug release, characterized by a pronounced burst followed by a slow sustained release, only slightly affected by the co-polymer architecture. This result was also confirmed with curve fitting via the Korsmeyer-Peppas model. Lastly, good antibacterial properties and biocompatibility exhibited in both star-shaped PCL-PEG co-polymers suggest a promising use for oral delivery applications.
Keywords: PCL arms; ciprofloxacin; drug delivery; hydrogels; star co-polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Boyd B.J., Bergström C.A., Vinarov Z., Kuentz M., Brouwers J., Augustijns P., Brandl M., Bernkop-Schnürch A., Shrestha N., Préat V., et al. Successful oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs both depends on the intraluminal behavior of drugs and of appropriate advanced drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019;137:104967. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.104967. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vinarov Z., Abrahamsson B., Artursson P., Batchelor H., Berben P., Bernkop-Schnürch A., Butler J., Ceulemans J., Davies N., Dupont D., et al. Current challenges and future perspectives in oral absorption research: An opinion of the UNGAP network. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021;171:289–331. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

