Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Control
- PMID: 37512723
- PMCID: PMC10384134
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14071412
Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Control
Abstract
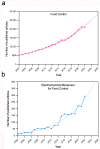
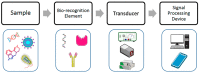
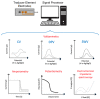
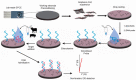
The rapid and sensitive detection of food contaminants is becoming increasingly important for timely prevention and treatment of foodborne disease. In this review, we discuss recent developments of electrochemical biosensors as facile, rapid, sensitive, and user-friendly analytical devices and their applications in food safety analysis, owing to the analytical characteristics of electrochemical detection and to advances in the design and production of bioreceptors (antibodies, DNA, aptamers, peptides, molecular imprinted polymers, enzymes, bacteriophages, etc.). They can offer a low limit of detection required for food contaminants such as allergens, pesticides, antibiotic traces, toxins, bacteria, etc. We provide an overview of a broad range of electrochemical biosensing designs and consider future opportunities for this technology in food control.
Keywords: aptasensor; detection; electrochemical sensor; food safety; genosensor; immunosensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO 2022. [(accessed on 1 March 2023)]. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gho-documents/world-health....
-
- WHO 2023. [(accessed on 1 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety.
-
- Morse T.D., Masuku H., Rippon S., Kubwalo H. Achieving an integrated approach to food safety and hygiene—Meeting the sustainable development goals in sub-saharan Africa. Sustainability. 2018;10:2394. doi: 10.3390/su10072394. - DOI
-
- Omerović N., Djisalov M., Živojević K., Mladenović M., Vunduk J., Milenković I., Knežević N.Ž., Gadjanski I., Vidić J. Antimicrobial nanoparticles and biodegradable polymer composites for active food packaging applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021;20:2428–2454. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12727. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

