Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation
- PMID: 37512934
- PMCID: PMC10383632
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11071762
Extracts from Wallis Sponges Inhibit Vibrio harveyi Biofilm Formation
Abstract
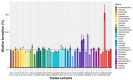
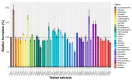
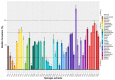
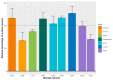
Pathogenic bacteria and their biofilms are involved in many human and animal diseases and are a major public health problem with, among other things, the development of antibiotic resistance. These biofilms are known to induce chronic infections for which classical treatments using antibiotic therapy are often ineffective. Sponges are sessile filter-feeding marine organisms known for their dynamic symbiotic partnerships with diverse microorganisms and their production of numerous metabolites of interest. In this study, we investigated the antibiofilm efficacy of different extracts from sponges, isolated in Wallis, without biocidal activity. Out of the 47 tested extracts, from 28 different genera, 11 showed a strong activity against Vibrio harveyi biofilm formation. Moreover, one of these extracts also inhibited two quorum-sensing pathways of V. harveyi.
Keywords: Vibrio harveyi; anti-biofilm activity; biofilm; marine natural products; sponge extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
- ANR-17-EURE-0015/Interdisciplinary graduate school for the blue planet
- FC is the recipient of a doctoral fellowship (PhD SPOQS project) co-funded by the Université de Bretagne Sud (UBS) and the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD)
- French Oceanographic Fleet, IRD, MNHN, Labex Mer and the Wallis and Futuna Environment Service
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

