Bi-MOF-Derived Carbon Wrapped Bi Nanoparticles Assembly on Flexible Graphene Paper Electrode for Electrochemical Sensing of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions
- PMID: 37513081
- PMCID: PMC10386677
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13142069
Bi-MOF-Derived Carbon Wrapped Bi Nanoparticles Assembly on Flexible Graphene Paper Electrode for Electrochemical Sensing of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
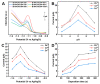
The development of nanohybrid with high electrocatalytic activity is of great significance for electrochemical sensing applications. In this work, we develop a novel and facile method to prepare a high-performance flexible nanohybrid paper electrode, based on nitrogen-doped carbon (NC) wrapped Bi nanoparticles (Bi-NPs) assembly derived from Bi-MOF, which are decorated on a flexible and freestanding graphene paper (GP) electrode. The as-obtained Bi-NPs encapsulated by an NC layer are uniform, and the active sites are increased by introducing a nitrogen source while preparing Bi-MOF. Owing to the synergistic effect between the high conductivity of GP electrode and the highly efficient electrocatalytic activity of Bi-NPs, the NC wrapped Bi-NPs (Bi-NPs@NC) modified GP (Bi-NPs@NC/GP) electrode possesses high electrochemically active area, rapid electron-transfer capability, and good electrochemical stability. To demonstrate its outstanding functionality, the Bi-NPs@NC/GP electrode has been integrated into a handheld electrochemical sensor for detecting heavy metal ions. The result shows that Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ can be detected with extremely low detection limits, wide linear range, high sensitivity, as well as good selectivity. Furthermore, it demonstrates outstanding electrochemical sensing performance in the simultaneous detection of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+. Finally, the proposed electrochemical sensor has achieved excellent repeatability, reproducibility, stability, and reliability in measuring real water samples, which will have great potential in advanced applications in environmental systems.
Keywords: Bi nanoparticles; electrochemical catalysis and sensing; flexible and freestanding graphene paper electrode; heavy metal ions detection; nitrogen-doped carbon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Ovidiu-Teodor M., Cornelia M., Alina Giorgiana B., Eleonora-Mihaela U., Mihaela C., Raluca I., George-Octavian B., Alexandru C.R. Electrochemistry of Rhodanine Derivatives as Model for New Colorimetric and Electrochemical Azulene Sensors for the Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Symmetry. 2023;15:752.
-
- Abdu N., Abdullahi A.A., Abdulkadir A. Heavy Metals and Soil Microbes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016;15:65–84. doi: 10.1007/s10311-016-0587-x. - DOI
-
- Elif Y., Akif A., Ahmet A. Land Application of Municipal Sewage Sludge: Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;319:128568.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

