Determination of Dicofol in Tea Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Coupled Chemometrics
- PMID: 37513164
- PMCID: PMC10386380
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28145291
Determination of Dicofol in Tea Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Coupled Chemometrics
Abstract
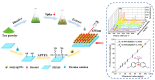
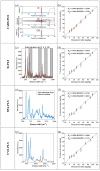
Dicofol is a highly toxic residual pesticide in tea, which seriously endangers human health. A method for detecting dicofol in tea by combining stoichiometry with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) technology was proposed in this study. AuNPs were prepared, and silver shells were grown on the surface of AuNPs to obtain core-shell Au@AgNPs. Then, the core-shell Au@AgNPs were attached to the surface of a PDMS membrane by physical deposition to obtain a Au@AgNPs/PDMS substrate. The limit of detection (LOD) of this substrate for 4-ATP is as low as 0.28 × 10-11 mol/L, and the LOD of dicofol in tea is 0.32 ng/kg, showing high sensitivity. By comparing the modeling effects of preprocessing and variable selection algorithms, it is concluded that the modeling effect of Savitzky-Golay combined with competitive adaptive reweighted sampling-partial least squares regression is the best (Rp = 0.9964, RPD = 10.6145). SERS technology combined with stoichiometry is expected to rapidly detect dicofol in tea without labels.
Keywords: Au@AgNPs/PDMS; SERS; chemometrics; dicofol; tea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fang J., Sureda A., Silva A.S., Khan F., Xu S.W., Nabavi S.M. Trends of tea in cardiovascular health and disease: A critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;88:385–396. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.001. - DOI
-
- Yang Z.Y., Baldermann S., Watanabe N. Recent studies of the volatile compounds in tea. Food Res. Int. 2013;53:585–599. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.02.011. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

