Evaluation of Four Adjuvant Combinations, IVAX-1, IVAX-2, CpG-1826+Montanide ISA 720 VG and CpG-1018+Montanide ISA 720 VG, for Safety and for Their Ability to Elicit Protective Immune Responses in Mice against a Respiratory Challenge with Chlamydia muridarum
- PMID: 37513710
- PMCID: PMC10383793
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12070863
Evaluation of Four Adjuvant Combinations, IVAX-1, IVAX-2, CpG-1826+Montanide ISA 720 VG and CpG-1018+Montanide ISA 720 VG, for Safety and for Their Ability to Elicit Protective Immune Responses in Mice against a Respiratory Challenge with Chlamydia muridarum
Abstract
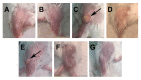
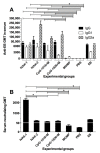
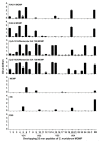
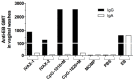
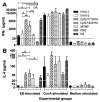
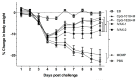
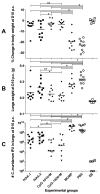
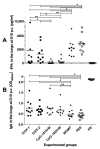
There is an urgent need to produce a vaccine for Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Here, using the Chlamydia muridarum major outer membrane protein (MOMP) as an antigen, four adjuvant combinations IVAX-1 (MPLA+CpG-1018+AddaVax), IVAX-2 (MPLA+CpG-1018+AS03), CpG-1826+Montanide ISA 720 VG (CpG-1826+Mont) and CpG-1018+Montanide ISA 720 VG (CpG-1018+Mont), were tested for their local reactogenicity and ability to elicit protection in BALB/c mice against a respiratory challenge with C. muridarum. Immunization with IVAX-1 or IVAX-2 induced no significant local reactogenicity following intramuscular immunization. In contrast, vaccines containing Montanide resulted in the formation of a local granuloma. Based on the IgG2a/IgG1 ratio in serum, the four adjuvant combinations elicited Th1-biased responses. IVAX-1 induced the highest in vitro neutralization titers while CpG-1018+Mont stimulated the lowest. As determined by the levels of IFN-γ produced by T-cells, the most robust cellular immune responses were elicited in mice immunized with CpG-1018+Mont, while the weakest responses were mounted by mice receiving IVAX-1. Following the respiratory challenge, mice immunized with CpG-1018+Mont lost the least amount of body weight and had the lowest number of C. muridarum inclusion-forming units (IFUs) in the lungs, while those receiving IVAX-2 had lost the most weight and had the highest number of IFUs in their lungs. Animals vaccinated with CpG-1826+Mont had the lightest lungs while those immunized using IVAX-2 had the heaviest. To conclude, due to their safety and adjuvanticity, IVAX formulations should be considered for inclusion in human vaccines against Chlamydia.
Keywords: Chlamydia muridarum; Chlamydia trachomatis; adjuvant combinations; major outer membrane protein; mice; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
We do not have any commercial or other association that might pose a conflict of interest (e.g., pharmaceutical stock ownership, consultancy, advisory board membership, relevant patents or research funding).
Figures
Similar articles
-
A vaccine formulated with a combination of TLR-2 and TLR-9 adjuvants and the recombinant major outer membrane protein elicits a robust immune response and significant protection against a Chlamydia muridarum challenge.Microbes Infect. 2014 Mar;16(3):244-52. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.11.009. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Microbes Infect. 2014. PMID: 24291713 Free PMC article.
-
Improved protection against Chlamydia muridarum using the native major outer membrane protein trapped in Resiquimod-carrying amphipols and effects in protection with addition of a Th1 (CpG-1826) and a Th2 (Montanide ISA 720) adjuvant.Vaccine. 2020 Jun 9;38(28):4412-4422. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.04.065. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32386746 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the safety and efficacy of recombinant Chlamydia muridarum MOMP vaccines, formulated with CpG-1826 and 70%, 50%, 30% or 10% concentrations of Montanide ISA-720 VG, to elicit protective immune responses against a C. muridarum respiratory challenge.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 11:rs.3.rs-3688658. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3688658/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Jun 10;9(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00880-6. PMID: 38168233 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Safety and efficacy of C. muridarum vaccines adjuvanted with CpG-1826 and four concentrations of Montanide-ISA-720-VG.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Jun 10;9(1):104. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00880-6. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38858418 Free PMC article.
-
A vaccine formulated with the major outer membrane protein can protect C3H/HeN, a highly susceptible strain of mice, from a Chlamydia muridarum genital challenge.Immunology. 2015 Nov;146(3):432-43. doi: 10.1111/imm.12520. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 26423798 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Progress towards effective vaccines for Chlamydia trachomatis.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 1;38(1):54-59. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000001075. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39745334 Review.
-
CT584 Is Not a Protective Vaccine Antigen against Respiratory Chlamydial Challenge in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Oct 3;12(10):1134. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101134. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460301 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation in mice of cell-free produced CT584 as a Chlamydia vaccine antigen.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 6:2024.06.04.597210. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597210. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895407 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Effects of prime-boost strategies on the protective efficacy and immunogenicity of a PLGA (85:15)-encapsulated Chlamydia recombinant MOMP nanovaccine.Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae004. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae004. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 38862192 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Assessment of Chlamydia trachomatis Major Outer Membrane Protein (MOMP)-Derived Vaccine Antigens and Immunological Profiling in Mice with Different Genetic Backgrounds.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;12(7):789. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070789. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC . Prevention DoS. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Atlanta, GE, USA: 2021. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2019; pp. 1–168.
-
- Schachter J., Dawson C.R. Human Chlamydial Infections. Volume xi. PSG Pub. Co.; Littleton, MA, USA: 1978. p. 273.
-
- Taylor H.R. Trachoma: A Blinding Scourge from the Bronze Age to the Twenty-First Century. 1st ed. Haddington Press Pry Ltd.; Melbourne, VIC, Australia: 2008.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

